
-
 Edwards leads Wolves past Grizzlies as playoff race heats up
Edwards leads Wolves past Grizzlies as playoff race heats up
-
Ancelotti questioned as Real Madrid face Alaves

-
 Old foes Bayern and Dortmund face off amid spectre of European exit
Old foes Bayern and Dortmund face off amid spectre of European exit
-
Early holiday, more fans: Philippines schools adapt to climate change

-
 In skies, as on land, European forces face gaps if US pulls back
In skies, as on land, European forces face gaps if US pulls back
-
Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?

-
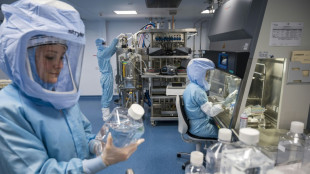 WHO pandemic agreement talks face deadline crunch
WHO pandemic agreement talks face deadline crunch
-
Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns

-
 LeMond hails 'one in a million' Pogacar ahead of Paris-Roubaix debut
LeMond hails 'one in a million' Pogacar ahead of Paris-Roubaix debut
-
Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts

-
 Trump admits trade war 'cost' as markets hit
Trump admits trade war 'cost' as markets hit
-
AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game

-
 Despite Trump pause, overall US tariff rate at highest in a century
Despite Trump pause, overall US tariff rate at highest in a century
-
'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims

-
 Panama deal allows US to deploy troops to canal
Panama deal allows US to deploy troops to canal
-
US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves

-
 Grieving Dominicans start burying 220 victims of nightclub disaster
Grieving Dominicans start burying 220 victims of nightclub disaster
-
Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National

-
 US auto union praises some Trump tariffs
US auto union praises some Trump tariffs
-
Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
-
 Rose: I've played well enough to win Masters but lack the jacket
Rose: I've played well enough to win Masters but lack the jacket
-
Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead

-
 Rose rockets to Masters lead, defending champ Scheffler in pursuit
Rose rockets to Masters lead, defending champ Scheffler in pursuit
-
Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi

-
 Oscars to add new award for stunts
Oscars to add new award for stunts
-
Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'

-
 'Mistakes can happen': Amorim backs Onana after Lyon nightmare
'Mistakes can happen': Amorim backs Onana after Lyon nightmare
-
RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'

-
 Tourist family, pilot killed in 'tragic' NY helicopter crash
Tourist family, pilot killed in 'tragic' NY helicopter crash
-
No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title

-
 Man Utd and Spurs draw in Europa League, Rangers hold Athletic
Man Utd and Spurs draw in Europa League, Rangers hold Athletic
-
Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit

-
 Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors in Europa League
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors in Europa League
-
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors

-
 Wall Street rally fizzles as tariff fears resurface
Wall Street rally fizzles as tariff fears resurface
-
MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study

-
 Argentina braves 24-hour strike as it awaits word on IMF loan
Argentina braves 24-hour strike as it awaits word on IMF loan
-
Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard

-
 Porro rescues Postecoglou as Spurs held by Frankfurt
Porro rescues Postecoglou as Spurs held by Frankfurt
-
Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster

-
 CONMEBOL proposes one-off 64-team World Cup in 2030
CONMEBOL proposes one-off 64-team World Cup in 2030
-
Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup

-
 Former Real Madrid coach Leo Beenhakker dies aged 82
Former Real Madrid coach Leo Beenhakker dies aged 82
-
Rose rockets to top of Masters leaderboard, Scheffler one back

-
 Langer fades after fiery start in Masters farewell
Langer fades after fiery start in Masters farewell
-
Iran, US raise stakes ahead of key talks in Oman

-
 US-China confrontation overshadows Trump's 'beautiful' trade war
US-China confrontation overshadows Trump's 'beautiful' trade war
-
RFK, MLK assassination files to be released in 'next few days'

-
 Relevent settle anti-trust lawsuit with US Soccer
Relevent settle anti-trust lawsuit with US Soccer
-
Orcas, dolphins stuck in closed French marine park


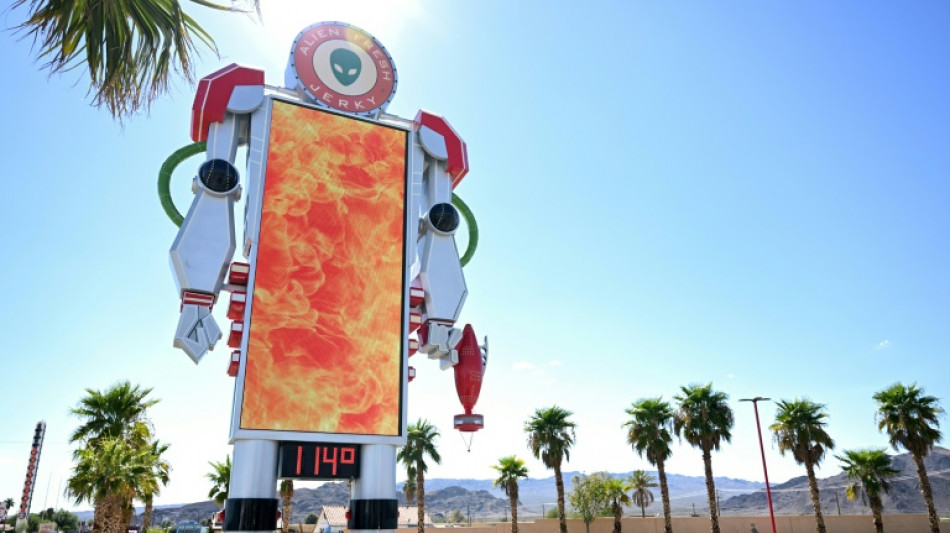
Heat waves: what you need to know
A blistering heat wave is baking the western United States, the latest to blast the northern hemisphere in a summer that has brought extreme temperatures across Europe, Asia and North America.
Climatologists say the kiln-like conditions in California, Nevada and Arizona are caused by a heat dome -- a huge bubble of stationary high pressure that is trapping ever-hotter air.
And, they say, human-caused climate change is making these oppressive heat waves worse -- hotter, longer and more frequent.
Here's what you need to know about heat waves.
- What is a heat wave? -
Anyone suffering through sultry nights and sweltering days knows they're in a heat wave, but there are a few technical definitions.
The one the US government chooses is: at least two consecutive days when the minimum temperature for the area is hotter than 85 percent of July and August days in the same area, based on historical averages.
That minimum usually comes at night, which is important -- after a very hot day, our bodies tend to cool off at night. But if the temperature remains elevated, that's much harder. This is when people get ill.
It's also important to localize the definition. People accustomed to 85 Fahrenheit (29 Celsius) days are likely not fazed by 90 degrees. But if you live in a chilly, damp spot and the mercury hits 90, you'll find it much harder to cope.
- What causes heat waves? -
Generally it's an area of high pressure that parks itself in one spot, forming a heat dome -- imagine a huge greenhouse that lets in the sun's heat, but won't let any air flow through.
The high pressure prevents clouds from forming as it pushes air downwards, compressing and heating the air -- think of how a tire gets hot as you pump more air in.
Jet streams -- air that flows high in the Earth's atmosphere -- usually move pressure systems around the planet.
But they can meander. As the waves of a jet stream widen, they slow and can even stop. This is what leaves a ridge of high pressure in one place.
- Are heat waves dangerous? -
Yes, very. More people die from the heat every year in the United States than from any other extreme weather, including floods, tornadoes, and cold snaps, according to government figures.
A ferocious heat wave in Spain and Portugal in July left more than 1,700 people dead.
And hundreds died last year when a heat wave frazzled Canada and the western US, with temperatures of up to 121F (49C).
When it's very hot, our bodies find it more difficult to keep cool, which can result in a "cascade of illnesses," according to the World Health Organization.
These include heat cramps, heat exhaustion, heatstroke, and hyperthermia.
"Deaths and hospitalizations from heat can occur extremely rapidly (same day), or have a lagged effect (several days later) and result in accelerating death or illness in the already frail," the WHO says.
That means anyone who already suffers from problems with their heart or respiratory system is particularly at risk.
The effects of intense heat are not evenly felt across societies, and tend to be more acute in poorer, and more marginalized communities.
Homeless people or those who work outside during the heat of the day are obviously at risk, but so are people living in neighborhoods without tree cover, or near to sources of pollution like roads.
- What is climate change doing? -
Like all weather phenomena, climate change is super-charging heat waves.
Human activity, specifically the burning of fossil fuels, has warmed the Earth by an average of around 1.9F (1.2C) since pre-industrial times. Much of this warming has happened in the last 50 years.
US government data shows heat waves worsening in concert with a warming planet: Every decade since the 1960s they have got longer, hotter and more frequent.
"Their frequency has increased steadily, from an average of two heat waves per year during the 1960s to six per year during the 2010s and 2020s," the Environmental Protection Agency says.
"In recent years, the average heat wave in major US urban areas has been about four days long. This is about a day longer than the average heat wave in the 1960s."
A study after last year's record-breaking heat wave in Canada found it would have been "virtually impossible" without human-caused climate change.
The World Weather Attribution group said that global warming, caused by greenhouse gas emissions, made the heat wave at least 150 times more likely to happen.
M.A.Colin--AMWN



