
-
 US tariffs could push up inflation, slow growth: Fed official
US tariffs could push up inflation, slow growth: Fed official
-
New Bruce Springsteen music set for June 27 release

-
 Tom Cruise pays tribute to Val Kilmer
Tom Cruise pays tribute to Val Kilmer
-
Mexico president welcomes being left off Trump's tariffs list

-
 Zuckerberg repeats Trump visits in bid to settle antitrust case
Zuckerberg repeats Trump visits in bid to settle antitrust case
-
US fencer disqualified for not facing transgender rival

-
 'Everyone worried' by Trump tariffs in France's champagne region
'Everyone worried' by Trump tariffs in France's champagne region
-
Italy's Brignone suffers broken leg with Winter Olympics looming

-
 Iyer blitz powers Kolkata to big IPL win over Hyderabad
Iyer blitz powers Kolkata to big IPL win over Hyderabad
-
Russian soprano Netrebko to return to London's Royal Opera House

-
 French creche worker gets 25 years for killing baby with drain cleaner
French creche worker gets 25 years for killing baby with drain cleaner
-
UK avoids worst US tariffs post-Brexit, but no celebrations

-
 Canada imposing 25% tariff on some US auto imports
Canada imposing 25% tariff on some US auto imports
-
Ruud wants 'fair share' of Grand Slam revenue for players

-
 Lesotho, Africa's 'kingdom in the sky' jolted by Trump
Lesotho, Africa's 'kingdom in the sky' jolted by Trump
-
Trump's trade math baffles economists

-
 Gaza heritage and destruction on display in Paris
Gaza heritage and destruction on display in Paris
-
'Unprecedented crisis' in Africa healthcare: report

-
 Pogacar gunning for blood and thunder in Tour of Flanders
Pogacar gunning for blood and thunder in Tour of Flanders
-
Macron calls for suspension of investment in US until tariffs clarified

-
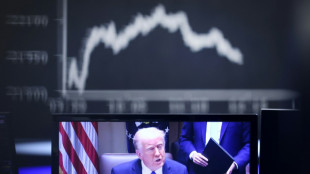 Wall St leads rout as world reels from Trump tariffs
Wall St leads rout as world reels from Trump tariffs
-
Mullins gets perfect National boost with remarkable four-timer

-
 Trump tariffs hammer global stocks, dollar and oil
Trump tariffs hammer global stocks, dollar and oil
-
Authors hold London protest against Meta for 'stealing' work to train AI

-
 Tate Modern gifted 'extraordinary' work by US artist Joan Mitchell
Tate Modern gifted 'extraordinary' work by US artist Joan Mitchell
-
Mexico president welcomes being left off Trump's new tariffs list

-
 Tonali eager to lead Newcastle back into Champions League
Tonali eager to lead Newcastle back into Champions League
-
Lesotho hardest hit as new US tariffs rattle Africa

-
 Stellantis pausing some Canada, Mexico production over Trump auto tariffs
Stellantis pausing some Canada, Mexico production over Trump auto tariffs
-
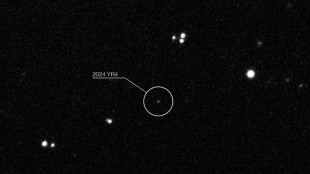
Rising odds asteroid that briefly threatened Earth will hit Moon
-
 Italy reels from Brignone broken leg with Winter Olympics looming
Italy reels from Brignone broken leg with Winter Olympics looming
-
Is the Switch 2 worth the price? Reviews are mixed

-
 Ancelotti’s tax trial wraps up in Spain with prosecutors seeking jail
Ancelotti’s tax trial wraps up in Spain with prosecutors seeking jail
-
Civilians act to bring aid to Myanmar earthquake victims

-
 US trade gap narrows in February ahead of bulk of Trump tariffs
US trade gap narrows in February ahead of bulk of Trump tariffs
-
Stocks, dollar and oil sink as gold hits high on Trump tariffs

-
 Countries eye trade talks as Trump tariff blitz roils markets
Countries eye trade talks as Trump tariff blitz roils markets
-
Arsenal defender Gabriel out for rest of the season

-
 Trump says US to emerge 'stronger' as markets tumble over tariffs
Trump says US to emerge 'stronger' as markets tumble over tariffs
-
Wiegman says Belgium games can aid England's women's Euros title defence

-
 Prosecutors demand jail term for Ancelotti for tax fraud
Prosecutors demand jail term for Ancelotti for tax fraud
-
Syria accuses Israel of deadly destabilisation campaign

-
 Skiing World Cup champion Brignone suffers broken leg
Skiing World Cup champion Brignone suffers broken leg
-
Iconic Paris hotel Lutetia taken over by Mandarin Oriental

-
 Nepal capital chokes as wildfires rage
Nepal capital chokes as wildfires rage
-
AI could impact 40 percent of jobs worldwide: UN

-
 'Shocking': US tariffs worse than feared for Vietnamese exporters
'Shocking': US tariffs worse than feared for Vietnamese exporters
-
Liverpool's Slot happy to let Premier League title bid take its course

-
 USA sole bidder for 2031 Women's World Cup, UK set to host in 2035
USA sole bidder for 2031 Women's World Cup, UK set to host in 2035
-
Tesla sales fall again in Germany amid Musk backlash

| CMSD | -0.73% | 22.665 | $ | |
| RBGPF | -0.41% | 67.72 | $ | |
| JRI | -1.64% | 12.83 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.99% | 22.28 | $ | |
| BCC | -7.76% | 94.72 | $ | |
| SCS | -5.91% | 10.82 | $ | |
| RIO | -2.29% | 58.56 | $ | |
| RELX | 0.98% | 51.485 | $ | |
| NGG | 5.41% | 69.54 | $ | |
| BCE | 3.09% | 22.515 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 0.2% | 9.8 | $ | |
| GSK | 3.52% | 39.015 | $ | |
| AZN | 2.6% | 74.145 | $ | |
| VOD | 2.72% | 9.375 | $ | |
| BTI | 4.33% | 42.07 | $ | |
| BP | -7.45% | 31.465 | $ |

Climate finance billions at stake at COP29
Rich nations will be under pressure at this month's UN COP29 conference to substantially increase the amount of money they give to poorer countries for climate action.
But there is deep disagreement over how much is needed, who should pay and what should be covered, ensuring that "climate finance" will top the agenda at COP29 in Baku.
- What is climate finance? -
It is the buzzword in this year's negotiations, which run from November 11 to 22, but there is not one agreed definition of climate finance.
In general terms, it is money spent in a manner "consistent with a pathway towards low greenhouse gas emissions and climate-resilient development", as per phrasing used in the Paris Agreement.
That includes government or private money for clean energy like solar and wind, technology like electric vehicles, or adaptation measures like dykes to hold back rising seas.
But could a subsidy for a new water-efficient hotel, for example, be counted? It is not something the COP summits have addressed directly.
At the annual UN negotiations, climate finance has come to refer to the difficulties the developing world faces getting the money it needs to prepare for global warming.
- Who pays? -
Under a 1992 UN accord, a handful of rich countries most responsible for global warming were obligated to provide finance.
In 2009, the United States, the European Union, Japan, Britain, Canada, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, New Zealand and Australia agreed to pay $100 billion per year by 2020.
They only achieved this for the first time in 2022. The delay eroded trust and fuelled accusations that rich countries were shirking their responsibility.
At COP29, nearly 200 nations are expected to agree on a new finance goal beyond 2025.
India has called for $1 trillion a year and some other proposals go higher, but countries on the hook want other major economies to chip in.
They argue times have changed and the big industrialised nations of the early 1990s represent just 30 percent of historic greenhouse gas emissions today.
In particular, there is a push for China -- the world's largest polluter today -- and the oil-rich Gulf countries to pay. They do not accept this proposal.
- What's being negotiated? -
Experts commissioned by the UN estimate that developing countries, excluding China, will need $2.4 trillion per year by 2030.
But the line between climate finance, foreign aid and private capital is often blurred and campaigners are pushing for clearer terms that specify where money comes from, and in what form.
In an October letter to governments, dozens of activist, environment and scientific groups called on rich nations to pay developing countries $1 trillion a year in three clear categories.
Some $300 billion would be government money for reducing planet-heating emissions, $300 billion for adaptation measures and $400 billion for disaster relief known as "loss and damage" funds.
The signatories said all the money should be grants, seeking to redress the provision of loans as climate finance that poorer countries say compounds their debt woes.
Developed countries do not want money for "loss and damage" included under any new climate finance pact reached at COP29.
- Where will they find the money? -
Today, most climate finance aid goes through development banks or funds co-managed with the countries concerned, such as the Green Climate Fund and the Global Environment Facility.
Campaigners are very critical of the $100 billion pledge because two-thirds of the money was given as loans, not grants.
Even revised upwards, it is likely any new pledge from governments will fall well short of what is needed.
But this commitment is viewed as highly symbolic nonetheless, and crucial to unlocking other sources of money, namely private capital.
Financial diplomacy also plays out at the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund and the G20, where this year's host Brazil wants to craft a global tax on billionaires.
The idea of new global taxes, for example on aviation or maritime transport, is also supported by France, Kenya and Barbados, with the backing of UN chief Antonio Guterres.
Redirecting fossil fuel subsidies towards clean energy or wiping the debt of poor countries in exchange for climate investments are also among the options.
COP29 host Azerbaijan, meanwhile, has asked fossil fuel producers to contribute to a new fund that would channel money to developing countries.
J.Williams--AMWN



