-
 Olympic push for kho kho, India's ancient tag sport
Olympic push for kho kho, India's ancient tag sport
-
Dangerous Fritz sets up Monfils clash at Australian Open

-
 AFP photographer's search for his mother in the Nazi camps
AFP photographer's search for his mother in the Nazi camps
-
Life after the unthinkable: Shoah survivors who began again in Israel

-
 Israeli cabinet to vote on Gaza ceasefire deal
Israeli cabinet to vote on Gaza ceasefire deal
-
Jabeur finds it 'hard to breathe' as asthma flares up in Melbourne

-
 Swiatek powers on as Sinner, Medevedev top men's Melbourne bill
Swiatek powers on as Sinner, Medevedev top men's Melbourne bill
-
Nintendo rumour mill in overdrive over new Switch

-
 Biden warns of Trump 'oligarchy' in dark farewell speech
Biden warns of Trump 'oligarchy' in dark farewell speech
-
Superb Swiatek sets up Raducanu showdown at Australian Open

-
 Asian stocks follow Wall St higher on welcome US inflation data
Asian stocks follow Wall St higher on welcome US inflation data
-
Toyota arm Hino makes deal to settle emission fraud case

-
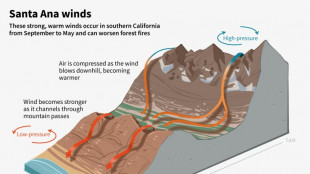
 Fire-wrecked Los Angeles gets a break as winds drop
Fire-wrecked Los Angeles gets a break as winds drop
-
Superb Swiatek races into third round at Australian Open

-
 Biden warns of dangerous 'oligarchy' in dark farewell speech
Biden warns of dangerous 'oligarchy' in dark farewell speech
-
Herbicide under US scrutiny over potential Parkinson's link

-
 South Korea's Yoon to avoid fresh questioning after dramatic arrest
South Korea's Yoon to avoid fresh questioning after dramatic arrest
-
Behind the Gaza deal: a US odd couple and last-minute snags

-
 Noisy racket on Australian Open 'party court' forces match move
Noisy racket on Australian Open 'party court' forces match move
-
AFP strikes deal for France's Mistral AI to use news articles

-
 'Sensational' Arsenal back in title race: Arteta
'Sensational' Arsenal back in title race: Arteta
-
Survivors count the mental cost of Los Angeles fires

-
 Arsenal reignite Premier League title charge as Isak stars again
Arsenal reignite Premier League title charge as Isak stars again
-
Thousands across Gaza celebrate ceasefire deal

-
 Postecoglou slams 'nowhere near good enough' Spurs after Arsenal defeat
Postecoglou slams 'nowhere near good enough' Spurs after Arsenal defeat
-
Moyes 'under no illusions' after defeat on Everton return

-
 Arsenal reignite Premier League title hopes as Isak stars again
Arsenal reignite Premier League title hopes as Isak stars again
-
Yamal drives dominant Barca past Betis into Copa del Rey quarters

-
 Arsenal fightback sinks Spurs to ignite title bid
Arsenal fightback sinks Spurs to ignite title bid
-
Qatar, US announce Gaza truce, hostage release deal

-
 US consumer inflation rises in December but underlying pressures ease
US consumer inflation rises in December but underlying pressures ease
-
McGregor accused of sexual assault in civil suit

-
 Inter's title defence slowed by draw with spirited Bologna
Inter's title defence slowed by draw with spirited Bologna
-
Isak fires Newcastle into Premier League top four, Moyes misery

-
 Sane hits brace as Bayern thump Hoffenheim
Sane hits brace as Bayern thump Hoffenheim
-
Aston Villa ruin Moyes' Everton return

-
 Norman replaced as CEO of LIV Golf
Norman replaced as CEO of LIV Golf
-
SpaceX delays latest Starship megarocket test to Thursday

-
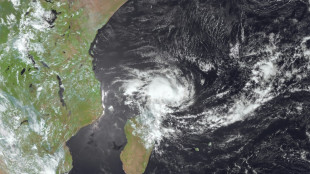
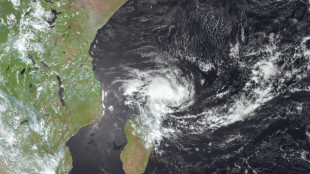
 Quake-stricken Vanuatu heads to polls in snap election
Quake-stricken Vanuatu heads to polls in snap election
-
Qatar, US announce Gaza truce, hostage release deal agreed

-
 Galaxy sign Zanka from Anderlecht
Galaxy sign Zanka from Anderlecht
-
Police probe abuse of Havertz's wife after Arsenal star's woes

-
 Drake files defamation suit against Universal over Kendrick Lamar track
Drake files defamation suit against Universal over Kendrick Lamar track
-
Qatar PM says Gaza truce, hostage release deal agreed

-
 US firms concerned about Trump tariff, immigration plans: Fed
US firms concerned about Trump tariff, immigration plans: Fed
-
Yellen warns against extending Trump's first-term US tax cuts

-
 Biden hails Gaza deal, says worked with Trump
Biden hails Gaza deal, says worked with Trump
-
US Supreme Court weighs Texas age-check for porn sites

-
 Brad Pitt isn't messaging you, rep warns, after adoring fan scammed
Brad Pitt isn't messaging you, rep warns, after adoring fan scammed
-
Trump's Energy Dept pick wants to develop renewables... and fossil fuels


Top science editor defends peer-review system in climate row
Top science journal Nature was hit with claims last week that its editors -– and those of other leading titles -– have a bias towards papers highlighting negative climate change effects. It denies the allegation.
Scientist Patrick Brown shocked his peers when he said he had tailored his study on California wildfires to emphasise global warming. He claimed it would not have been accepted if it had not pandered to editors' preferred climate "narrative".
Nature's editor-in-chief Magdalena Skipper spoke to AFP about the case and the broader challenges facing academic publishing in the age of climate change and artificial intelligence.
The interview has been edited for length and flow.
- Bias claim -
Q. Are journal editors biased towards studies that emphasise the role of climate change over other factors?
A. "The allegation that the only reason why (Patrick Brown) got the paper published in Nature was because he chose the results to fit a specific narrative makes no sense at all. I'm completely baffled (by the claim). If a researcher provides compelling, convincing, robust evidence that goes against a consensus, that study actually becomes of special interest to us -- that's how science progresses.
"Since (climate change) is a pressing issue, of course there is an awful lot of research that is funded, performed and subsequently published to probe the matter, to understand how grave the problem really is today.
"In this case we had (peer-) reviewers saying that climate change is not the only factor that affects wildfires. The author himself argued that, for the purpose of this paper, he wished to retain the focus solely on climate change.
"We were persuaded that a paper with that focus was of value to the research community because of the contribution made by the quantification (of climate impacts)."
- Studies retracted -
Q. Research shows thousands of published studies across the academic world get retracted due to irregularities. Is the peer-review system fit for purpose?
A. "I think everyone in the scientific community would agree that the peer review system isn't perfect, but it's the best system we have. No system is 100-percent perfect, which is why at Nature, we have been trialling different approaches to peer review. There can be many rounds of peer review. Its complexity depends on the comments of the reviewers. We may decide not to pursue the paper.
"We have had cases at Nature of deliberate scientific misconduct, where somebody manipulates or fabricates data. It happens across disciplines, across scientific publishing. This is extremely rare.
"I think the fact that we see retractions is actually a signal that a system works."
- Pressure to publish -
Q. Is there too much pressure on scientists to get published at any cost?
A. "Science funding is precious and scarce, let's face it. Researchers have to compete for funding. Once an investigation has been funded and carried out, it makes sense for the results to be published.
"On the other hand, PhD students in many educational systems are required to publish one or more scientific papers before they graduate. Is this a helpful requirement when we know that a large proportion of PhD students are not going to continue in research?
"In many cases, early-career researchers waste time, opportunity and money to publish in predatory journals (that, unlike Nature, take a fee without offering proper peer review and editing), where their reputation suffers. They are effectively tricked into thinking that they are genuinely publishing to share information with the community."
- AI in publishing -
Q. What measures is Nature taking to monitor the use of artificial intelligence programs in producing scientific studies?
A. "We do not disallow using LLMs (large-language models such as ChatGPT) as a tool in preparation of manuscripts. We certainly disallow the use of LLMs as co-authors. We want the authors who have availed themselves of some AI tool in the process to be very clear about it. We have published and continue to publish papers where AI was used in the research process.
"I've heard of journals which published papers where leftover text from (AI tool) prompts was included in papers. At Nature, this would be spotted by the editors. But when we work with the research community and the authors who submit to us, there is an element of trust. If we find that this trust has been abused consistently then we may have to resort to some systematic way of scanning for generative AI use."
Q. Do editors have the technical means to scan for use of these AI tools?
A. At the moment, not to my knowledge. It's an incredibly fast-moving field. These generative AI tools are themselves evolving. There are also some really promising applications of AI in accelerating research itself.
S.F.Warren--AMWN