
-
 Mbappe can be Real Madrid 'legend' like Ronaldo: Ancelotti
Mbappe can be Real Madrid 'legend' like Ronaldo: Ancelotti
-
Saka 'ready to go' for Arsenal after long injury lay-off: Arteta

-
 Aston Martin to sell stake in Formula One team
Aston Martin to sell stake in Formula One team
-
Three talking points ahead of clay-court season

-
 French court hands Le Pen five-year election ban
French court hands Le Pen five-year election ban
-
Probe accuses ex J-pop star Nakai of sexual assault

-
 Japan leads hefty global stock market losses on tariff woes
Japan leads hefty global stock market losses on tariff woes
-
Saka 'ready to go' after long injury lay-off: Arteta

-
 Ingebrigtsen Sr, on trial for abusing Olympic champion, says he was 'overly protective'
Ingebrigtsen Sr, on trial for abusing Olympic champion, says he was 'overly protective'
-
Tourists and locals enjoy 'ephemeral' Tokyo cherry blossoms

-
 Khamenei warns of 'strong' response if Iran attacked
Khamenei warns of 'strong' response if Iran attacked
-
France fines Apple 150 million euros over privacy feature

-
 UK PM urges nations to smash migrant smuggling gangs 'once and for all'
UK PM urges nations to smash migrant smuggling gangs 'once and for all'
-
Thai authorities probe collapse at quake-hit construction site

-
 France's Le Pen convicted in fake jobs trial
France's Le Pen convicted in fake jobs trial
-
Chinese tech giant Huawei says profits fell 28% last year

-
 Trump says confident of TikTok deal before deadline
Trump says confident of TikTok deal before deadline
-
Myanmar declares week of mourning as hopes fade for quake survivors

-
 Japan's Nikkei leads hefty market losses, gold hits record
Japan's Nikkei leads hefty market losses, gold hits record
-
Tears in Taiwan for relatives hit by Myanmar quake

-
 Venezuela says US revoked transnational oil, gas company licenses
Venezuela says US revoked transnational oil, gas company licenses
-
'Devastated': Relatives await news from Bangkok building collapse

-
 Arsenal, Tottenham to play pre-season North London derby in Hong Kong
Arsenal, Tottenham to play pre-season North London derby in Hong Kong
-
Japan's Nikkei leads hefty equity market losses; gold hits record

-
 Israel's Netanyahu picks new security chief, defying legal challenge
Israel's Netanyahu picks new security chief, defying legal challenge
-
Trump says US tariffs to hit 'all countries'

-
 Prayers and tears for Eid in quake-hit Mandalay
Prayers and tears for Eid in quake-hit Mandalay
-
After flops, movie industry targets fresh start at CinemaCon

-
 Tsunoda targets podium finish in Japan after 'unreal' Red Bull move
Tsunoda targets podium finish in Japan after 'unreal' Red Bull move
-
French chefs await new Michelin guide

-
 UK imposes travel permit on Europeans from Wednesday
UK imposes travel permit on Europeans from Wednesday
-
At his academy, Romanian legend Hagi shapes future champions

-
 Referee's lunch break saved Miami winner Mensik from early exit
Referee's lunch break saved Miami winner Mensik from early exit
-
Djokovic refuses to discuss eye ailment after shock Miami loss

-
 Mitchell magic as Cavs bag 60th win, Pistons and T'Wolves brawl
Mitchell magic as Cavs bag 60th win, Pistons and T'Wolves brawl
-
Mensik shocks Djokovic to win Miami Open

-
 Duterte lawyer: 'compelling' grounds to throw case out
Duterte lawyer: 'compelling' grounds to throw case out
-
What happens on Trump's 'Liberation Day' and beyond?

-
 Clock ticks on Trump's reciprocal tariffs as countries seek reprieve
Clock ticks on Trump's reciprocal tariffs as countries seek reprieve
-
Japan-Australia flagship hydrogen project stumbles

-
 Musk deploys wealth in bid to swing Wisconsin court vote
Musk deploys wealth in bid to swing Wisconsin court vote
-
Mensik upsets Djokovic to win Miami Open

-
 China manufacturing activity grows at highest rate in a year
China manufacturing activity grows at highest rate in a year
-
'Waited for death': Ex-detainees recount horrors of Sudan's RSF prisons

-
 Japan's Nikkei leads big losses in Asian markets as gold hits record
Japan's Nikkei leads big losses in Asian markets as gold hits record
-
Rescue hopes fading three days after deadly Myanmar quake

-
 'Basketbrawl' as seven ejected in Pistons-Wolves clash
'Basketbrawl' as seven ejected in Pistons-Wolves clash
-
Four men loom large in Microsoft history

-
 Computer pioneer Microsoft turns 50 in the age of AI
Computer pioneer Microsoft turns 50 in the age of AI
-
Trump calls out both Putin and Zelensky over ceasefire talks


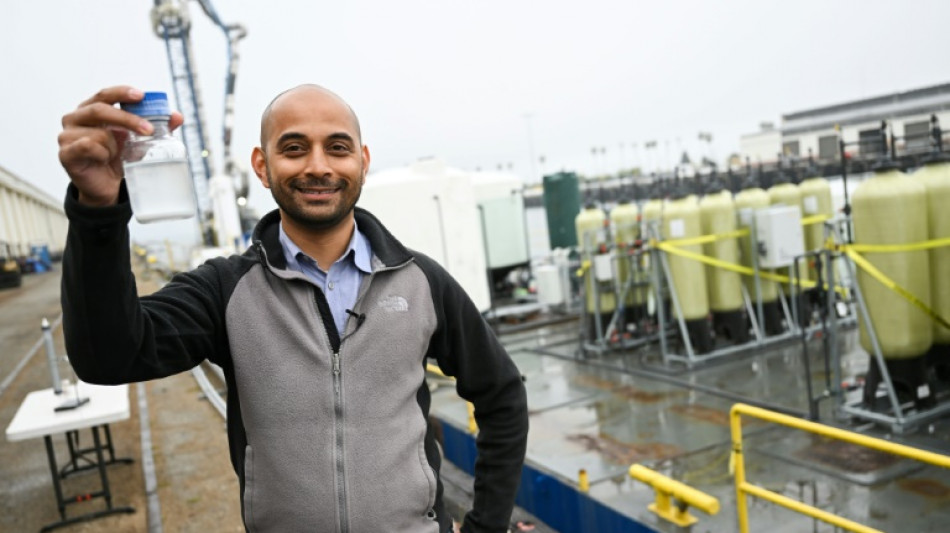
'Big sponge': new CO2 tech taps oceans to tackle global warming
Floating in the port of Los Angeles, a strange-looking barge covered with pipes and tanks contains a concept that scientists hope to make waves: a new way to use the ocean as a vast carbon dioxide sponge to tackle global warming.
Scientists from University of California Los Angeles (UCLA) have been working for two years on SeaChange -- an ambitious project that could one day boost the amount of CO2, a major greenhouse gas, that can be absorbed by our seas.
Their goal is "to use the ocean as a big sponge," according to Gaurav Sant, director of the university's Institute for Carbon Management (ICM).
The oceans, covering most of the Earth, are already the planet's main carbon sinks, acting as a critical buffer in the climate crisis.
They absorb a quarter of all CO2 emissions, as well as 90 percent of the warming that has occurred in recent decades due to increasing greenhouse gases.
But they are feeling the strain. The ocean is acidifying, and rising temperatures are reducing its absorption capacity.
The UCLA team wants to increase that capacity by using an electrochemical process to remove vast quantities of CO2 already in seawater -- rather like wringing out a sponge to help recover its absorptive power.
"If you can take out the carbon dioxide that is in the oceans, you're essentially renewing their capacity to take additional carbon dioxide from the atmosphere," Sant told AFP.
- Trapped -
Engineers built a floating mini-factory on a 100-foot (30-meter) long boat which pumps in seawater and subjects it to an electrical charge.
Chemical reactions triggered by electrolysis convert CO2 dissolved in the seawater into a fine white powder containing calcium carbonate -- the compound found in chalk, limestone and oyster or mussel shells.
This powder can be discarded back into the ocean, where it remains in solid form, thereby storing CO2 "very durably... over tens of thousands of years," explained Sant.
Meanwhile, the pumped water returns to the sea, ready to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Sant and his team are confident the process will not damage the marine environment, although this will require further testing to confirm.
A potential additional benefit of the technology is that it creates hydrogen as a byproduct. As the so-called "green revolution" progresses, the gas could be widely used to power clean cars, trucks and planes in the future.
Of course, the priority in curbing global warming is for humans to drastically reduce current CO2 emissions -- something we are struggling to achieve.
But in parallel, most scientists say carbon dioxide capture and storage techniques can play an important role in keeping the planet livable.
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) could help to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 as it offsets emissions from industries which are particularly difficult to decarbonize, such as aviation, and cement and steel production.
It could help to tackle the stocks of CO2 that have been accumulating in the atmosphere for decades.
- 'Promising solution' -
Keeping global warming under control will require the removal of between 450 billion and 1.1 trillion tons of CO2 from the atmosphere by 2100, according to the first global report dedicated to the topic, released in January.
That would require the CDR sector "to grow at a rate of about 30 percent per year over the next 30 years, much like what happened with wind and solar," said one of its authors, Gregory Nemet.
UCLA's SeaChange technology "fits into a category of a promising solution that could be large enough to be climate-relevant," said Nemet, a professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
By sequestering CO2 in mineral form within the ocean, it differs markedly from existing "direct air capture" (DAC) methods, which involve pumping and storing gas underground through a highly complex and expensive process.
A start-up company, Equatic, plans to scale up the UCLA technology and prove its commercial viability, by selling carbon credits to manufacturers wanting to offset their emissions.
In addition to the Los Angeles barge, a similar boat is currently being tested in Singapore.
Sant hopes data from both sites will quickly lead to the construction of far larger plants that are capable of removing "thousands of tons of carbon" each year.
"We expect to start operating these new plants in 18 to 24 months," he said.
O.M.Souza--AMWN



