
-
 Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations
Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations
-
'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong

-
 DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
-
England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown

-
 Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah
Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah
-
McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours

-
 Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller
Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller
-
Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle

-
 Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League
Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League
-
Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis

-
 Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
-
'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear

-
 Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit
Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit
-
Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling

-
 PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season
PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season
-
Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show

-
 14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player
14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player
-
Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller

-
 Zverev sets up birthday bash with Shelton in Munich
Zverev sets up birthday bash with Shelton in Munich
-
Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller

-
 US Supreme Court intervenes to pause Trump deportations
US Supreme Court intervenes to pause Trump deportations
-
Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final

-
 US, Iran to hold more nuclear talks after latest round
US, Iran to hold more nuclear talks after latest round
-
Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show

-
 Bayern close in on Bundesliga title with Heidenheim thumping
Bayern close in on Bundesliga title with Heidenheim thumping
-
Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial

-
 Putin announces 'Easter truce' in Ukraine
Putin announces 'Easter truce' in Ukraine
-
McLaren duo in ominous show of force in Saudi final practice

-
 Afghan PM condemns Pakistan's 'unilateral' deportations
Afghan PM condemns Pakistan's 'unilateral' deportations
-
Iran says to hold more nuclear talks with US after latest round

-
 Comeback queen Liu leads US to World Team Trophy win
Comeback queen Liu leads US to World Team Trophy win
-
Buttler fires Gujarat to top of IPL table in intense heat

-
 Unimpressive France stay on course for Grand Slam showdown
Unimpressive France stay on course for Grand Slam showdown
-
Shelton fights past Cerundolo to reach Munich ATP final

-
 Vance and Francis: divergent values but shared ideas
Vance and Francis: divergent values but shared ideas
-
Iran, US conclude second round of high-stakes nuclear talks in Rome

-
 Dumornay gives Lyon first leg lead over Arsenal in women's Champions League semis
Dumornay gives Lyon first leg lead over Arsenal in women's Champions League semis
-
Trans rights supporters rally outside UK parliament after landmark ruling

-
 Rune destroys Khachanov to reach Barcelona Open final
Rune destroys Khachanov to reach Barcelona Open final
-
From Messi to Trump, AI action figures are the rage

-
 Vance discusses migration during Vatican meeting with pope's right-hand man
Vance discusses migration during Vatican meeting with pope's right-hand man
-
Afghan FM tells Pakistan's top diplomat deportations are 'disappointment'

-
 British cycling icon Hoy and wife provide solace for each other's ills
British cycling icon Hoy and wife provide solace for each other's ills
-
Money, power, violence in high-stakes Philippine elections

-
 Iran, US hold second round of high-stakes nuclear talks in Rome
Iran, US hold second round of high-stakes nuclear talks in Rome
-
Japanese warships dock at Cambodia's Chinese-renovated naval base

-
 US Supreme Court pauses deportation of Venezuelans from Texas
US Supreme Court pauses deportation of Venezuelans from Texas
-
Pakistan foreign minister arrives in Kabul as Afghan deportations rise

-
 Heat and Grizzlies take final spots in the NBA playoffs
Heat and Grizzlies take final spots in the NBA playoffs
-
Iran, US to hold second round of high-stakes nuclear talks in Rome


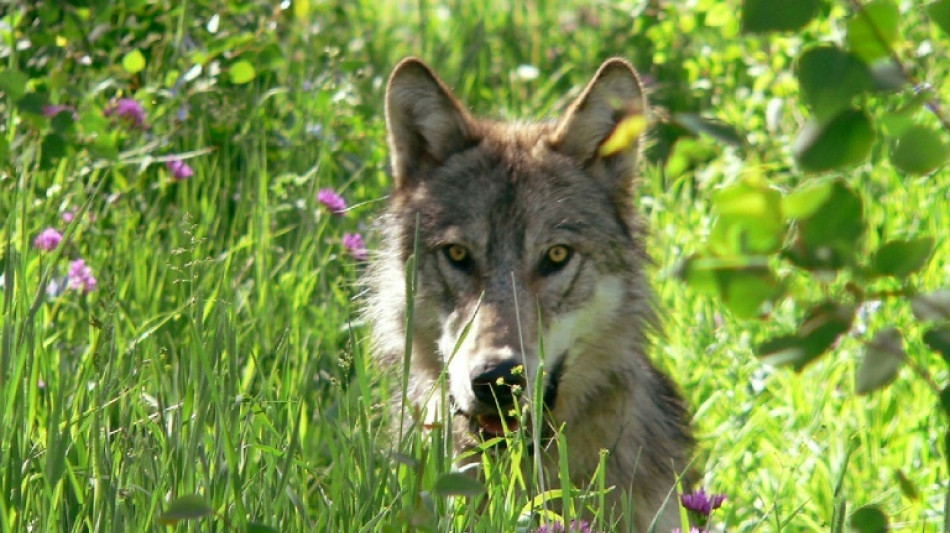
Wolves emboldened by parasite more likely to lead pack: study
Wolves infected with a common parasite are far more likely to become the leader of their pack, according to a new study, suggesting that the brain-dwelling intruder emboldens its host to take more risks.
The single-celled parasite, Toxoplasma gondii, only sexually reproduces in cats but can infect all warm-blooded animals.
Between 30-50 percent of people worldwide are estimated to be infected with the parasite, which remains for life as dormant tissue cysts. However people with a healthy immune system rarely have any symptoms.
While some studies have reported an association between people having the parasite in their brain and increased risk-taking, other research has disputed these findings and no definitive link has been proven.
The new study, published in the journal Communications Biology on Thursday, took advantage of 26 years' worth of data on grey wolves living in the Yellowstone National Park in the United States to investigate how the parasite could affect their behaviour.
The researchers from the Yellowstone Wolf Project analysed the blood samples of nearly 230 wolves and 62 cougars -- the big cats are known spreaders of the parasite.
They found that infected wolves were more likely to foray deeper into cougar territory than uninfected wolves.
Infected wolves were also 11 times more likely to leave their pack than wolves without the parasite, the study said, indicating a higher rate of risk-taking.
And an infected wolf is up to 46 times more likely to become pack leader, the researchers estimated, adding that the role is normally won by more aggressive animals.
Study co-author Kira Cassidy told AFP that while "being bolder is not necessarily a bad thing," it can "lower survival for the most bold animals as they might make decisions that put them in danger more often."
"Wolves do not have the survival space to take too many more risks than they already do."
Cassidy said it was only the second study on T. gondii's effect on a wild animal, after research last year found increased boldness in infected hyena cubs made them more likely to get closer to -- and killed by -- lions in Kenya.
Laboratory research has also found that rodents with the parasite lose their instinctual fear of cats -- driving them into the hands of the only host where T. gondii can reproduce.
William Sullivan, a professor of pharmacology and toxicology at the Indiana University School of Medicine who has been studying T.gondii for more than 25 years, called the wolf paper "a rare gem".
However he warned that such an observational study could not show causation.
"A wolf that is a born risk-taker may simply be more likely to venture into cougar territory and contract Toxoplasma," he said.
But "if the findings are correct, they suggest we may be underestimating the impact Toxoplasma has on ecosystems around the world," he added.
- What about humans? -
"That's the million-dollar question," Sullivan said, adding that "no one knows for sure and the literature is mixed".
Ajai Vyas, a T. gondii expert at Singapore's Nanyang Technological University, warned against inferring that infection could increase risk-taking in people.
"There is a lot about human behaviour that is different from other animals," he told AFP.
People often get infected by T. gondii from eating undercooked meat -- or via their pet cat, particularly when cleaning out their litter boxes.
In some cases, especially in people with weakened immune systems, T. gondii can lead to toxoplasmosis, a disease that can cause brain and eye damage.
P.M.Smith--AMWN



