
-
 Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
-
Tariffs could lift Boeing and Airbus plane prices even higher

-
 Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big MLS crowd in Cleveland

-
 Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
-
'Pandora's box': alarm bells in Indonesia over rising military role

-
 Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
-
Trio share lead at tight LA Championship

-
 Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
-
Recovering pope expected to delight crowds at Easter Sunday mass

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
-
Force skipper clueless about extra-time rules in pulsating Super Rugby draw

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big crowd in Cleveland

-
 Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
-
Another round of anti-Trump protests hits US cities

-
 'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
-
PSG maintain unbeaten Ligue 1 record, Marseille back up to second

-
 US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to block Trump deportations

-
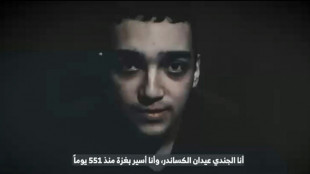 Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
-
Pacers thump Bucks to open NBA playoffs

-
 Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
-
Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations

-
 'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
-
DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
-
 England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
-
Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah

-
 McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
-
Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
-
Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League

-
 Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
-
Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling

-
 'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
-
Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit

-
 Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
-
PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season

-
 Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
-
14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player

-
 Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
-
Zverev sets up birthday bash with Shelton in Munich

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller
Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to pause Trump deportations

-
 Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final
Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final
-
US, Iran to hold more nuclear talks after latest round

-
 Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show
-
Bayern close in on Bundesliga title with Heidenheim thumping

-
 Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial
Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial
-
Putin announces 'Easter truce' in Ukraine


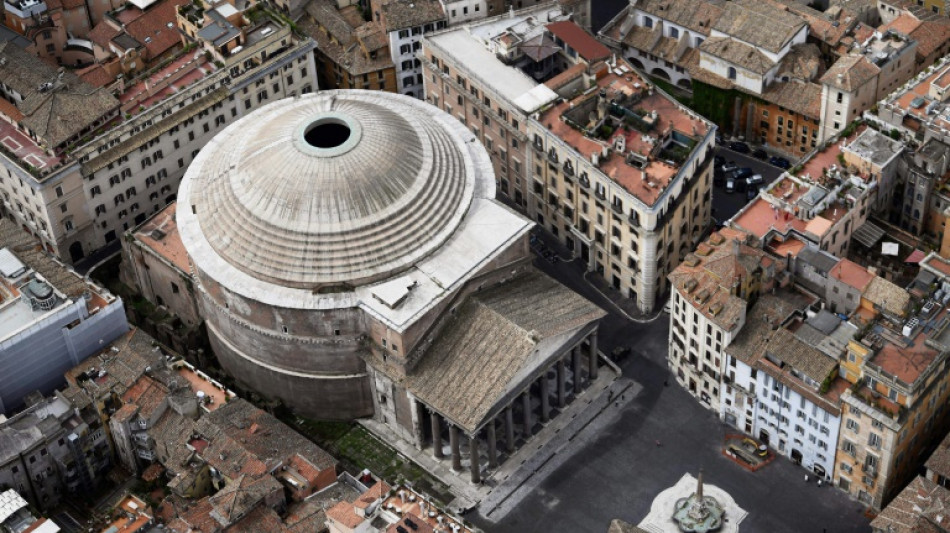
Researchers dig up secrets of 'self-healing' Roman concrete
How have Rome's ancient aqueducts and architectural marvels such as the Pantheon, which features the world's largest unreinforced concrete dome, endured the test of time?
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and other institutions believe they have uncovered the mystery of the durability of the 2,000-year-old structures -- self-healing concrete.
The secret lies in an ingredient of the ancient concrete used by the Romans that the researchers, whose findings are published in the latest edition of the journal Science Advances, said has been overlooked in previous studies.
The durability of the concrete used by the Romans has most frequently been attributed to the use of volcanic ash from Pozzuoli on the Bay of Naples, which was shipped across the Roman empire for construction.
But the researchers focused their attention on another component of the ancient concrete mix, small white chunks called "lime clasts."
"Ever since I first began working with ancient Roman concrete, I've always been fascinated by these features," said MIT professor of civil and environmental engineering Admir Masic, an author of the study.
"These are not found in modern concrete formulations, so why are they present in these ancient materials?"
The researchers said the lime clasts had been thought to be the result of "sloppy mixing practices" or poor-quality raw materials.
But they are in fact what gives the ancient concrete a "previously unrecognized self-healing capability."
"The idea that the presence of these lime clasts was simply attributed to low quality control always bothered me," said Masic.
"If the Romans put so much effort into making an outstanding construction material... why would they put so little effort into ensuring the production of a well-mixed final product?"
For the study, the researchers examined 2,000-year-old Roman concrete samples from the masonry mortar of a city wall in Privernum, Italy.
They found that a process known as "hot mixing" is what gave the concrete its "super-durable nature" in which the Romans mixed quicklime with water and the volcanic ash at high temperatures.
"The benefits of hot mixing are twofold," Masic said.
"First, when the overall concrete is heated to high temperatures, it allows chemistries that are not possible if you only used slaked lime, producing high-temperature-associated compounds that would not otherwise form.
"Second, this increased temperature significantly reduces curing and setting times since all the reactions are accelerated, allowing for much faster construction," he said.
It is the lime clasts that give the ancient concrete its "self-healing functionality," according to the research team, which also included scientists from Switzerland and Italy.
Tiny cracks in the concrete would tend to travel through the high-surface-area lime clasts and, when exposed to water, would recrystallize as calcium carbonate, filling the crack almost like glue.
"These reactions take place spontaneously and therefore automatically heal the cracks before they spread," said the researchers, who conducted tests using modern concrete and the ancient formula.
X.Karnes--AMWN



