
-
 Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
-
Tariffs could lift Boeing and Airbus plane prices even higher

-
 Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big MLS crowd in Cleveland

-
 Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
-
'Pandora's box': alarm bells in Indonesia over rising military role

-
 Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
-
Trio share lead at tight LA Championship

-
 Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
-
Recovering pope expected to delight crowds at Easter Sunday mass

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
-
Force skipper clueless about extra-time rules in pulsating Super Rugby draw

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big crowd in Cleveland

-
 Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
-
Another round of anti-Trump protests hits US cities

-
 'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
-
PSG maintain unbeaten Ligue 1 record, Marseille back up to second

-
 US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to block Trump deportations

-
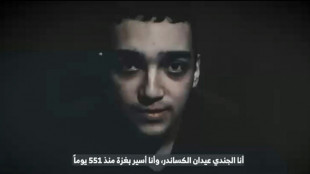 Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
-
Pacers thump Bucks to open NBA playoffs

-
 Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
-
Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations

-
 'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
-
DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
-
 England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
-
Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah

-
 McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
-
Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
-
Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League

-
 Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
-
Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling

-
 'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
-
Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit

-
 Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
-
PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season

-
 Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
-
14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player

-
 Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
-
Zverev sets up birthday bash with Shelton in Munich

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller
Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to pause Trump deportations

-
 Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final
Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final
-
US, Iran to hold more nuclear talks after latest round

-
 Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show
-
Bayern close in on Bundesliga title with Heidenheim thumping

-
 Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial
Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial
-
Putin announces 'Easter truce' in Ukraine


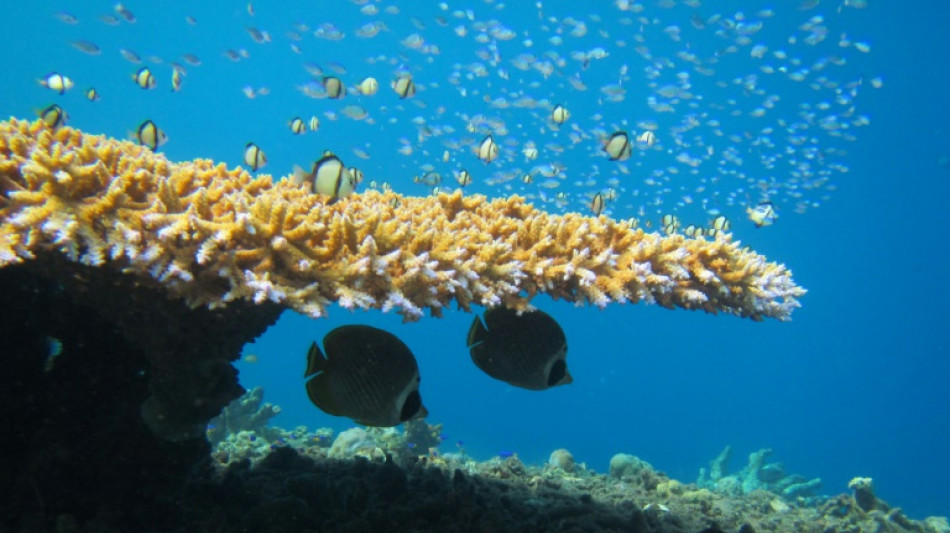
Coral bleaching causing 'unnecessary' fish fights
Fish that have lost food due to mass coral bleaching are getting into more unnecessary fights, causing them to expend precious energy and potentially threatening their survival, new research said Wednesday.
With the future of the world's coral reefs threatened by climate change, a team of researchers studied how a mass bleaching event affected 38 species of butterflyfish.
The colourfully patterned reef fish are the first to feel the effect of bleaching because they eat coral, so their "food source is hugely diminished really quickly", said Sally Keith, a marine ecologist at Britain's Lancaster University.
Keith and her colleagues had no idea a mass bleaching event was coming when they first studied the fish at 17 reefs off Japan, the Philippines, Indonesia and Christmas Island.
But when one of history's worst global bleaching events struck in 2016, it offered "the perfect opportunity" to study how it affected the fish's behaviour, Keith told AFP.
The researchers returned within a year and were "shocked" to see the devastation of the once beautiful reefs, she said.
Donning their snorkels or scuba gear, the team watched the fish "swimming around looking for food that just isn't there anymore," she added.
"There was a bit of crying in our masks."
- Losing battle -
The bleaching particularly affected Acropora coral, the main food source for the butterflyfish.
That "changed the playing field of who's eating what," Keith said, putting different species of butterflyfish in increased competition for other types of coral.
When a butterflyfish wants to signal to a competitor that a particular bit of coral is theirs, they point their noses down and raise their spiny dorsal fins.
"It's almost like raising your hackles," Keith said.
If that fails, one fish will chase the other, usually until the other gives up.
"I followed one for about 50 metres (165 feet) once, that was quite tiring, they're very fast," Keith said.
The team observed 3,700 encounters between butterflyfish.
Before the coral bleaching event, different species of butterflyfish were able to resolve disputes using signalling around 28 percent of the time.
But that number fell to just 10 percent after the bleaching, indicating many "unnecessary attacks," according to the new study in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
"Making poor decisions about who to fight, and where to invest their really valuable energy, could be that little bit that tips them over the edge towards actual starvation," said Keith, the study's lead author.
It is not clear if the fish will be able to adapt to the changes brought about by coral bleaching quickly enough, the researchers warned.
It could also have knock-on effects between species and up the food chain, she added.
Human-driven climate change has spurred mass coral bleaching as the world's oceans get warmer.
Modelling research last year found that even if the Paris climate goal of holding global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius is reached, 99 percent of the world's coral reefs will not be able to recover. At two degrees of warming, the number rose to 100 percent.
P.Mathewson--AMWN



