-
 South Korea's Lee meets Xi with trade, Pyongyang on the agenda
South Korea's Lee meets Xi with trade, Pyongyang on the agenda
-
Gauff shocked in United Cup, comeback kid Hurkacz stuns Zverev

-
 Tech firms lead markets higher, oil swings after Maduro ouster
Tech firms lead markets higher, oil swings after Maduro ouster
-
Defending Brisbane champion Lehecka wins tough opener

-
 Maduro's fall tests Venezuela's ruling 'club'
Maduro's fall tests Venezuela's ruling 'club'
-
'I can't walk anymore': Afghans freeze to death on route to Iran

-
 UK starts ban on junk food ads on daytime TV and online
UK starts ban on junk food ads on daytime TV and online
-
Trump declares US 'in charge' of Venezuela and Maduro goes to court

-
 Two killed in series of Russian attacks on Ukraine
Two killed in series of Russian attacks on Ukraine
-
Kasatkina feels pressure to 'repay Australia' after Russia switch

-
 Suns stun NBA-best Thunder as East-leading Pistons top Cavs
Suns stun NBA-best Thunder as East-leading Pistons top Cavs
-
China's birth-rate push sputters as couples stay child-free

-
 'Not about condoms': Chinese shrug off contraceptive tax
'Not about condoms': Chinese shrug off contraceptive tax
-
Root's majestic 160 powers England to 384 in final Ashes Test

-
 Chalamet boosts Oscar bid with Critics Choice Awards win
Chalamet boosts Oscar bid with Critics Choice Awards win
-
'Tuna King' pays record $3.2 mn for bluefin at Tokyo auction

-
 Tech firms lead Asian markets higher, oil swings after Maduro ouster
Tech firms lead Asian markets higher, oil swings after Maduro ouster
-
Cricket Australia boss hits out at 'archaic' bad light rules

-
 Trump insists 'we need Greenland'
Trump insists 'we need Greenland'
-
Century-maker Root steers England to 336-6 in final Ashes Test

-
 'Free our president', Maduro supporters demand at rally
'Free our president', Maduro supporters demand at rally
-
Danish PM calls on US to stop 'threatening' Greenland

-
 North Korea tests hypersonic missiles, says nuclear forces ready for war
North Korea tests hypersonic missiles, says nuclear forces ready for war
-
Root in Ponting territory with 41st Test century at 5th Ashes Test

-
 Guan Huat Seng Holdings Berhad Launches IPO Prospectus To Drive Next Phase Of Growth
Guan Huat Seng Holdings Berhad Launches IPO Prospectus To Drive Next Phase Of Growth
-
Apex Receives Exploration Permit for Rift REE Project, Nebraska; Drill Program Preparation Underway

-
 South Korea's Lee to meet Xi with trade, Pyongyang on the agenda
South Korea's Lee to meet Xi with trade, Pyongyang on the agenda
-
Messi's Miami sign Canada goalkeeper St. Clair

-
 Pistons top Cavs as Pacers' NBA misery continues
Pistons top Cavs as Pacers' NBA misery continues
-
Gonzalo treble helps Real Madrid thrash Betis, Atletico hopes dented

-
 Djokovic quits players' union he co-founded
Djokovic quits players' union he co-founded
-
Anne Frank's step-sister, Holocaust survivor Eva Schloss dies

-
 France's Le Garrec inspires La Rochelle to Toulon rout
France's Le Garrec inspires La Rochelle to Toulon rout
-
Hosts Morocco reach AFCON quarter-finals as Cameroon knock out South Africa

-
 Inter Milan reclaim Serie A summit
Inter Milan reclaim Serie A summit
-
Atletico title hopes dented in Real Sociedad draw

-
 Doue, Dembele light up first Paris derby in over 35 years
Doue, Dembele light up first Paris derby in over 35 years
-
Swiss grieve as all fire victims identified -- half of them under 18

-
 Panthers advance to NFL playoffs after Falcons beat Saints
Panthers advance to NFL playoffs after Falcons beat Saints
-
Cameroon end South Africa hopes to reach AFCON last eight

-
 'A gift' to be back, says Rodri despite Man City stumble
'A gift' to be back, says Rodri despite Man City stumble
-
Colombian guerrillas vow to confront US 'imperialism'

-
 Morocco lose injured playmaker Ounahi for rest of AFCON bid
Morocco lose injured playmaker Ounahi for rest of AFCON bid
-
Trump threatens new Venezuela leader after raid to seize Maduro

-
 Man City title hopes hit by managerless Chelsea
Man City title hopes hit by managerless Chelsea
-
Man City held by Chelsea in major title blow, Liverpool denied in Fulham thriller

-
 Managerless Chelsea dent Man City title hopes
Managerless Chelsea dent Man City title hopes
-
Ekitike's absence in Fulham draw leaves Slot with threadbare options

-
 Delcy Rodriguez: From Maduro's 'tigress' to acting Venezuelan president
Delcy Rodriguez: From Maduro's 'tigress' to acting Venezuelan president
-
Frank defends Johnson sale after Spurs jeered in Sunderland draw


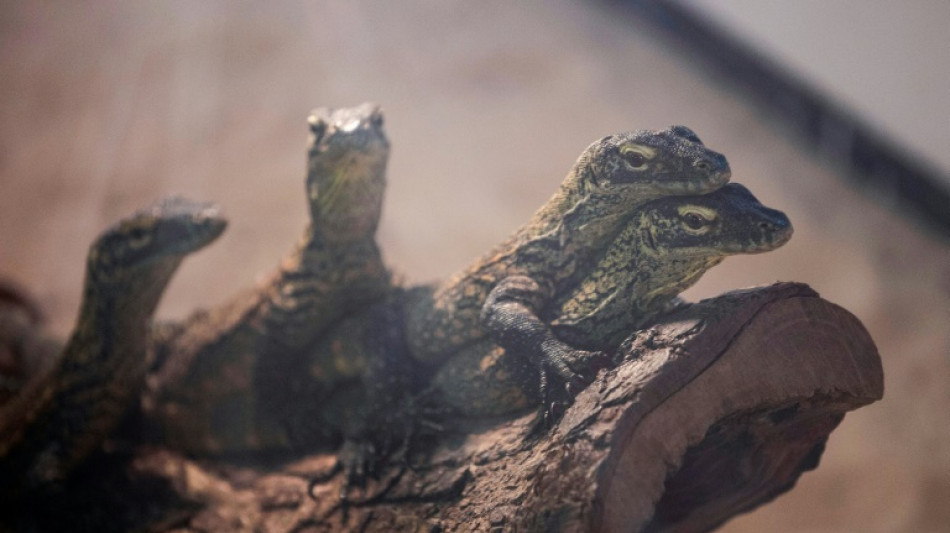
Half of species not assessed for endangered list risk extinction: study
More than half of species whose endangered status cannot be assessed due to a lack of data are predicted to face the risk of extinction, according to a machine-learning analysis published Thursday.
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) currently has nearly 150,000 entries on its Red List for threatened species, including some 41,000 species threatened with extinction.
These include 41 percent of amphibians, 38 percent of sharks and rays, 33 percent of reef building corals, 27 percent of mammals and 13 percent of birds.
But there are thousands of species that the IUCN has been unable to categorise as they are "data insufficient" and are not on the Red List even though they live in the same regions and face similar threats to those species that have so far been assessed.
Researchers from the Norwegian University of Science and Technology used a machine learning technique to predict the likelihood of 7,699 data deficient species being at risk of extinction.
They trained the algorithm on a list of more than 26,000 species that the IUCN has been able to categorise, incorporating data on the regions where species live and other factors known to influence biodiversity to determine whether it predicted their extinction risk status.
"These could include climatic conditions, land use conditions or land use changes, pesticide use, threats from invasive species or really a range of different stressors," lead author Jan Borgelt, from the university's Industrial Ecology Programme, told AFP.
After comparing the algorithm's results with the IUCN's lists, the team then applied it to predict the data deficient species' extinction risk.
Writing in the journal Communications Biology, they found that 4,336 species -- or 56 percent of those sampled -- were likely threatened with extinction, including 85 percent of amphibians and 61 percent of mammals.
This compares to the 28 percent of species assessed by the IUCN Red List.
"We see that across most land areas and coastal areas around the world that the average extinction risk would be higher if we included data deficient species," said Borgelt.
A global United Nations biodiversity assessment in 2019 warned that as many as a million species were threatened with extinction due to a number of factors including habitat loss, invasive species and climate change.
Borgelt said the analysis revealed some hotspots for data-deficient species risk, including Madagascar and southern India. He said he hoped the study could help the IUCN develop its strategy for underreported species, adding that the team had reached out to the union.
"With these predictions from machine learning we can get really sort of pre-assessments or we could use those as predictions to prioritise which species have to be looked at by the IUCN," he said.
Head of the IUCN's Red List Craig Hilton-Taylor said the organisation was continuously harnessing new technology with a view to reduce the number of data deficient species.
"We also understand that a proportion of data deficient species are at risk of extinction, and include this in our calculations when we estimate the proportion of threatened species in a group," he told AFP.
A.Jones--AMWN