
-
 Trump suggests Tesla vandals be jailed in El Salvador
Trump suggests Tesla vandals be jailed in El Salvador
-
Trump denies reports Musk to receive 'top secret' China briefing

-
 Germany's huge spending package passes final hurdle in upper house
Germany's huge spending package passes final hurdle in upper house
-
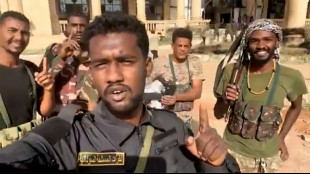
Sudan army recaptures presidential palace from RSF
-
 Turkey braces for day three of protests over Istanbul mayor's arrest
Turkey braces for day three of protests over Istanbul mayor's arrest
-
Russian central bank holds key rate at two-decade high

-
 French actor Depardieu goes on trial on sexual assault charges
French actor Depardieu goes on trial on sexual assault charges
-
Israeli opposition appeals against intel chief sacking

-
 French Olympic boss rules out new term after failed IOC bid
French Olympic boss rules out new term after failed IOC bid
-
Stock markets extend losses as Trump's tariffs hit global outlook

-
 Japan panel drafts response plan for Mount Fuji eruption
Japan panel drafts response plan for Mount Fuji eruption
-
As euphoria of victory fades, IOC chief Coventry faces geopolitical reality

-
 Namibia inaugurates its first woman president
Namibia inaugurates its first woman president
-
Eddie Jordan remembered as 'heart and soul of party' as Aston pay tribute

-
 Nawaz smacks record-breaking maiden ton as Pakistan win 3rd NZ T20
Nawaz smacks record-breaking maiden ton as Pakistan win 3rd NZ T20
-
'Gobsmacked' Hamilton smashes Shanghai lap record for first Ferrari pole

-
 Wood hits hat-trick as rampant New Zealand move to brink of World Cup
Wood hits hat-trick as rampant New Zealand move to brink of World Cup
-
Ferrari's Hamilton takes stunning pole for Chinese GP sprint

-
 Markets skid into weekend as trade fears cast a pall
Markets skid into weekend as trade fears cast a pall
-
Mosquito-borne chikungunya kills two in France's La Reunion

-
 Chapman blasts New Zealand to 204 in third Pakistan T20
Chapman blasts New Zealand to 204 in third Pakistan T20
-
Wood hat-trick as rampant New Zealand move to brink of World Cup

-
 Court rules against K-pop group NewJeans in contract dispute
Court rules against K-pop group NewJeans in contract dispute
-
Sudan army says retakes presidential palace from RSF

-
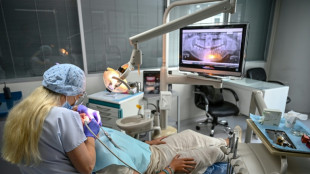 Turkish clinics vie for UK medical tourists' custom in London
Turkish clinics vie for UK medical tourists' custom in London
-
Red Bull's Horner fondly recalls 'heart and soul of party' Eddie Jordan

-
 London's Heathrow: Europe's biggest airport
London's Heathrow: Europe's biggest airport
-
Italy's Diaz dominates triple jump for opening world indoor gold

-
 Butler triple-double leads Warriors over Raptors as Curry hurt
Butler triple-double leads Warriors over Raptors as Curry hurt
-
In Washington, glum residents struggle with Trump return

-
 'People are afraid': NY migrant economy wilts under Trump policies
'People are afraid': NY migrant economy wilts under Trump policies
-
Norris quickest in China GP practice ahead of sprint qualifying

-
 Ronen Bar: ex-Shin Bet chief who incurred right-wing wrath
Ronen Bar: ex-Shin Bet chief who incurred right-wing wrath
-
Khawaja lashes out at 'untrue' comments in growing availability row

-
 Kluivert vows response after nightmare start to Indonesia reign
Kluivert vows response after nightmare start to Indonesia reign
-
London's Heathrow airport closed after fire causes major power cut

-
 Taiwan's existential battle against Chinese spies
Taiwan's existential battle against Chinese spies
-
England eye eighth successive Women's Six Nations in World Cup build-up

-
 Toulouse begin Top 14 life without Dupont at title rivals Bordeaux-Begles
Toulouse begin Top 14 life without Dupont at title rivals Bordeaux-Begles
-
Japan core inflation slows to 3% in Feburary

-
 Trump's call for AI deregulation gets strong backing from Big Tech
Trump's call for AI deregulation gets strong backing from Big Tech
-
Vinicius fires stoppage time winner for Brazil

-
 Asian markets skid into weekend as trade fears cast a pall
Asian markets skid into weekend as trade fears cast a pall
-
Son says he 'let my team-mates down' in South Korea qualifying draw

-
 Forbidden K-pop to centre stage: North Koreans set for music debut
Forbidden K-pop to centre stage: North Koreans set for music debut
-
Panama stun 'painful' USA to reach Nations League final

-
 Italian paper prints fully-AI edition, but not to 'kill' journalism
Italian paper prints fully-AI edition, but not to 'kill' journalism
-
Netflix hit 'Adolescence' stokes UK parents' anxiety

-
 Blues coach sees signs of life after poor start to Super Rugby season
Blues coach sees signs of life after poor start to Super Rugby season
-
Saudi Arabia frees prisoners in apparent easing of crackdown


Infants remember more than you think, new study reveals
Our earliest years are a time of rapid learning, yet we typically cannot recall specific experiences from that period -- a phenomenon known as infantile amnesia.
A new study published in Science on Thursday challenges assumptions about infant memory, showing that young minds do indeed form memories. The question remains, however, why these memories become difficult to retrieve later in life.
"I've always been fascinated by this mysterious blank spot we have in our personal history," Nick Turk-Browne, professor of psychology at Yale and the study's senior author, told AFP.
Around the age of one, children become extraordinary learners -- acquiring language, walking, recognizing objects, understanding social bonds, and more. "Yet we remember none of those experiences -- so there's a sort of mismatch between this incredible plasticity and learning ability that we have," he said.
Sigmund Freud, the founder of psychoanalysis, hypothesized that early memories are repressed, though science has since largely dismissed the idea of an active suppression process. Instead, modern theories focus on the hippocampus, a part of the brain critical for episodic memory, which is not fully developed in infancy.
Turk-Browne, however, was intrigued by clues from previous behavioral research. Since babies cannot verbally report memories before acquiring language, their tendency to gaze longer at familiar things provides important hints.
Recent rodent studies monitoring brain activity have also shown that engrams -- patterns of cells that store memories -- form in the infant hippocampus but become inaccessible over time -- though they can be artificially reawakened through a technique that uses light to stimulate neurons.
But until now, pairing observations of infants with brain imaging had been out of reach, as babies are famously uncooperative when it comes to sitting still inside a Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) machine -- the device that tracks blood flow to "see" brain activity.
- Psychedelic patterns -
To overcome this challenge, Turk-Browne's team used methods his lab has refined over the years -- working with families to incorporate pacifiers, blankets, and stuffed animals; holding babies still with pillows; and using psychedelic background patterns to keep them engaged.
Still, inevitable wiggling led to blurry images that had to be discarded, but the team accounted for this by running hundreds of sessions.
In total, 26 infants participated -- half under a year old, half over -- while their brains were scanned during a memory task adapted from adult studies.
First, they were shown images of faces, scenes, or objects. Later, after viewing other images, they were presented with a previously seen image alongside a new one.
"We quantify how much time they spend looking at the old thing they've seen before, and that's a measure of their memory for that image," said Turk-Browne.
By comparing brain activity during successful memory formation versus forgotten images, the researchers confirmed that the hippocampus is active in memory encoding from a young age.
This was true for 11 of 13 infants over a year old but not for those under one. They also found that babies who performed best on memory tasks showed greater hippocampal activity.
"What we can conclude accurately from our study is that infants have the capacity to encode episodic memories in the hippocampus starting around one year of age," said Turk-Browne.
- Forgotten Memories -
"The ingenuity of their experimental approach should not be understated," researchers Adam Ramsaran and Paul Frankland wrote in an accompanying Science editorial.
But what remains unresolved is what happens to these early memories. Perhaps they are never fully consolidated into long-term storage -- or perhaps they persist but become inaccessible.
Turk-Browne suspects the latter and is now leading a new study testing whether infants, toddlers, and children can recognize video clips recorded from their own perspective as younger babies.
Early, tentative results suggest these memories might persist until around age three before fading. Turk-Browne is particularly intrigued by the possibility that such fragments could one day be reactivated later in life.
O.Karlsson--AMWN


