-
 Mozambique cyclone cluster raises fears of new norm
Mozambique cyclone cluster raises fears of new norm
-
DR Congo ceasefire terms still unclear after surprise summit

-
 UniCredit CEO says prepared to wait on Commerzbank decision
UniCredit CEO says prepared to wait on Commerzbank decision
-
Fleeing civilians fill Gaza roads as Israel keeps up strikes

-
 After Putin-Trump call, Russians dream of 1945-style Ukraine victory
After Putin-Trump call, Russians dream of 1945-style Ukraine victory
-
Global music business raked in $29.6 bn in 2024: report

-
 Ukraine, Russia claim neither heeding halt to energy strikes
Ukraine, Russia claim neither heeding halt to energy strikes
-
Rangers 'embarrassed' by racist banner charge from UEFA

-
 USL aims to bring promotion and relegation to USA
USL aims to bring promotion and relegation to USA
-
Santander to close one fifth of UK branches amid online switch

-
 Samaranch unruffled by China links on eve of IOC presidential vote
Samaranch unruffled by China links on eve of IOC presidential vote
-
Ohtani hits home run as Dodgers sweep Cubs in Tokyo

-
 Italy says six dead, 40 missing after migrant shipwreck
Italy says six dead, 40 missing after migrant shipwreck
-
Algerian boxer Khelif 'not intimidated' by Trump as she targets second Olympic gold in LA

-
 Record numbers forced to flee climate disasters: UN
Record numbers forced to flee climate disasters: UN
-
'Living in dictatorship': Istanbul mayor's arrest sparks anger

-
 Russia threatens the entire EU, bloc's chief tells AFP
Russia threatens the entire EU, bloc's chief tells AFP
-
French billionaire Bollore targeted in fraud case over Africa ports

-
 'Dark universe detective' telescope releases first data
'Dark universe detective' telescope releases first data
-
Stock markets diverge, gold hits high tracking global unrest

-
 Son says fit and firing as South Korea close on World Cup spot
Son says fit and firing as South Korea close on World Cup spot
-
China's Tencent sees profits surge as AI drive accelerates

-
 Hamas says open to talks as Israel keeps up Gaza strikes
Hamas says open to talks as Israel keeps up Gaza strikes
-
Turkey detains Istanbul mayor, Erdogan's main rival

-
 Endo says Japan won't be satisfied just to reach World Cup
Endo says Japan won't be satisfied just to reach World Cup
-
Toy trouble: Vietnam pulls dolls over South China Sea map

-
 Zelensky accuses Russia of rejecting ceasefire after new strikes
Zelensky accuses Russia of rejecting ceasefire after new strikes
-
Myanmar relief camps receive last WFP aid as cuts begin

-
 Markets mixed as geopolitics, trade wars deplete sentiment
Markets mixed as geopolitics, trade wars deplete sentiment
-
Zelensky accuses Russia of rejecting ceasefire as new strikes hit Ukraine

-
 Bank of Japan holds rates and warns of trade uncertainty
Bank of Japan holds rates and warns of trade uncertainty
-
Australia prepare for unknown against Kluivert's Indonesia

-
 Uganda: the quiet power in the eastern DRC conflict
Uganda: the quiet power in the eastern DRC conflict
-
Tech firms fight to stem deepfake deluge

-
 Rwanda, DRC presidents hold surprise ceasefire talks in Qatar
Rwanda, DRC presidents hold surprise ceasefire talks in Qatar
-
In US, a pastry chef attempts to crack an egg-free menu

-
 Nigerian Senate sexism row exposes uphill battle for women's rights
Nigerian Senate sexism row exposes uphill battle for women's rights
-
UK pagans have spring in their step as equinox approaches

-
 Kosovo inn serves up peace and love, one bite at a time
Kosovo inn serves up peace and love, one bite at a time
-
Rocked by Trump, EU seeks to kickstart defence push

-
 Ecuador declares 'force majeure' emergency, cuts exports over oil spill
Ecuador declares 'force majeure' emergency, cuts exports over oil spill
-
Turkey police detain Istanbul mayor, Erdogan's main rival

-
 Clippers rally to beat Cavaliers, Warriors and Celtics win
Clippers rally to beat Cavaliers, Warriors and Celtics win
-
'More united' China on Saudi revenge mission in World Cup qualifier

-
 France tries Cambodian ex-PM's guards over 1997 massacre
France tries Cambodian ex-PM's guards over 1997 massacre
-
New generation of Afghan women shift from burqa

-
 Malaysia's Silicon Valley ambitions face tough challenges
Malaysia's Silicon Valley ambitions face tough challenges
-
Duplantis headlines as world indoors finally get Nanjing green light

-
 'Hurting' New Zealand determined to reach World Cup, says coach
'Hurting' New Zealand determined to reach World Cup, says coach
-
Asian markets mixed as geopolitics, trade wars deplete sentiment


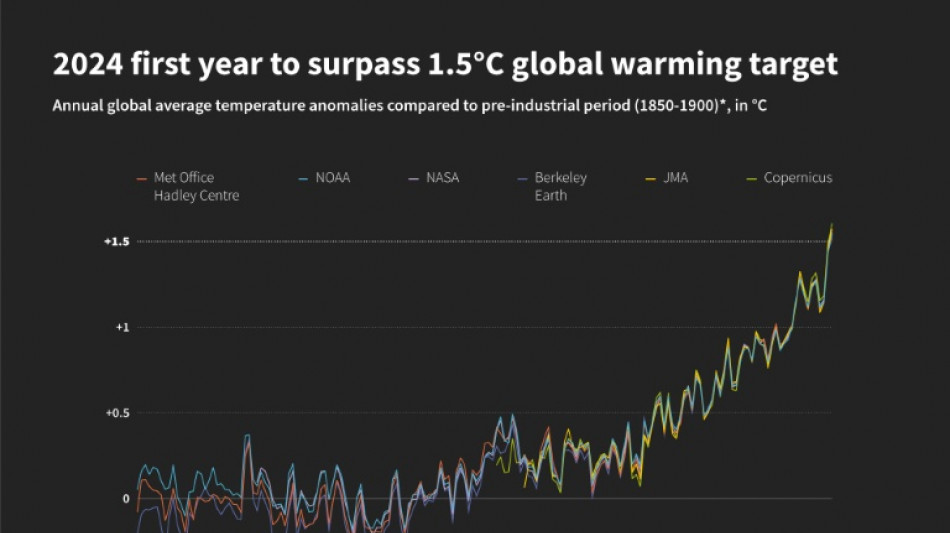
Record numbers forced to flee climate disasters: UN
Hundreds of thousands of people were forced to flee climate disasters last year, the United Nations said Wednesday, highlighting the urgent need for early warning systems covering the entire planet.
Poorer countries are severely affected by cyclones, droughts, wildfires and other disasters, according to the State of the Global Climate annual report by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), the UN's weather and climate agency.
The WMO said the record number of people fleeing climate disasters was based on figures from the International Displacement Monitoring Centre (IDMC), which has been collecting data on the subject since 2008.
In Mozambique, around 100,000 people were displaced by Cyclone Chido.
But wealthy countries were also hit, with the WMO pointing to the floods in the Spanish city of Valencia, which killed 224 people, and the devastating fires in Canada and the United States which forced more than 300,000 people to flee their homes in search of safety.
"In response, WMO and the global community are intensifying efforts to strengthen early warning systems and climate services," said the agency's chief Celeste Saulo.
The WMO wants everyone in the world covered by such systems by the end of 2027.
"We are making progress but need to go further and need to go faster. Only half of all countries worldwide have adequate early warning systems," said Saulo.
- Investment call -
The call comes two months after the return to power of US President Donald Trump -- a climate sceptic -- raised fears of a setback in climate science.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) -- the leading US agency responsible for weather forecasting, climate analysis and marine conservation -- has become a target for Trump's administration, with hundreds of scientists and experts already let go.
Trump has reappointed meteorologist Neil Jacobs to lead NOAA, despite him, during Trump's first term, being officially censured for bowing to political pressure and misleading the public about a hurricane forecast.
In recent weeks, the WMO has highlighted how essential NOAA and the United States are to a vast system put in place decades ago to monitor weather and the climate globally.
"We are working together with all the scientists around the world and the countries," Omar Baddour, who heads the WMO's climate monitoring and policy services division, said at the report's launch.
"We hope that this will continue, despite the differences in politics and internal changes."
Scientists and environmental advocates have voiced concern about layoffs and a possible dismantling of the NOAA.
Saulo said investment in weather, water and climate services was now more important than ever to build safer, more resilient communities.
- Planet issuing 'distress signals' -
Besides underlining the massive economic and social upheavals from extreme weather, the State of the Global Climate report said climate change indicators had once again reached record levels.
"The clear signs of human-induced climate change reached new heights in 2024, with some of the consequences being irreversible over hundreds if not thousands of years," the WMO said.
The 2015 Paris climate accords aimed to limit global warming to well below two degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels -- and to 1.5C if possible.
The report said 2024 was the warmest year in the 175-year observational record, and the first calendar year over the 1.5C threshold, with the global mean near-surface temperature 1.55C above the 1850-1900 average, according to an analysis compiling the six major international datasets.
"Our planet is issuing more distress signals -- but this report shows that limiting long-term global temperature rise to 1.5C is still possible," UN chief Antonio Guterres said.
Temperatures are only one part of the picture.
In 2024, "our oceans continued to warm and sea levels continued to rise", said Saulo.
Meanwhile the frozen parts of the Earth's surface are melting at an alarming rate, the WMO chief added.
"Glaciers continue to retreat, and Antarctic sea ice reached its second-lowest extent ever recorded," she said.
During the report's presentation, oceanographer Karina von Schuckmann highlighted the "acceleration" in two global indicators: ocean warming, which has accelerated since 1960, and sea level rise.
L.Mason--AMWN
