
-
 Ageless beauty contest: South African grannies strut the catwalk
Ageless beauty contest: South African grannies strut the catwalk
-
Trump says 'possibility' of meeting Putin for Ukraine talks in Turkey

-
 Gauff sees off Andreeva to reach Italian Open semis
Gauff sees off Andreeva to reach Italian Open semis
-
Merz vows to rev up German economic 'growth engine'

-
 Strikes kill 29 in Gaza, amid hostage release talks
Strikes kill 29 in Gaza, amid hostage release talks
-
Tennis champ Sinner meets Pope Leo, offers quick rally

-
 England sees driest spring since 1956: government agency
England sees driest spring since 1956: government agency
-
Trump presses Syria leader on Israel ties after lifting sanctions

-
 Rare blue diamond fetches $21.5 mn at auction in Geneva
Rare blue diamond fetches $21.5 mn at auction in Geneva
-
Stock markets fluctuate as China-US trade euphoria fades

-
 Ousted Myanmar envoy charged with trespass in London residence row
Ousted Myanmar envoy charged with trespass in London residence row
-
Russia jails prominent vote monitor for five years

-
 Umbro owner in joint bid for Le Coq Sportif
Umbro owner in joint bid for Le Coq Sportif
-
Tom Cruise has world guessing as he unleashes 'Mission: Impossible' at Cannes

-
 China's Tencent posts forecast-beating Q1 revenue on gaming growth
China's Tencent posts forecast-beating Q1 revenue on gaming growth
-
Trump presses Syria leader on Israel relations after lifting sanctions

-
 FA appoint former Man Utd sporting director Dan Ashworth as chief football officer
FA appoint former Man Utd sporting director Dan Ashworth as chief football officer
-
Stop holding opponents incommunicado, UN experts tell Venezuela

-
 Indonesian filmmakers aim to impress at Cannes
Indonesian filmmakers aim to impress at Cannes
-
Trump presses Syria leader on Israel after lifting sanctions

-
 French PM to testify on child abuse scandal
French PM to testify on child abuse scandal
-
Players stuck in middle with IPL, national teams on collision course

-
 Peru PM quits ahead of no-confidence vote
Peru PM quits ahead of no-confidence vote
-
Strikes kill 29 in Gaza as hostage release talks ongoing

-
 Court raps Brussels for lack of transparency on von der Leyen vaccine texts
Court raps Brussels for lack of transparency on von der Leyen vaccine texts
-
France summons cryptocurrency businesses after kidnappings
-
 Pakistan returns Indian border guard captured after Kashmir attack
Pakistan returns Indian border guard captured after Kashmir attack
-
Baidu plans self-driving taxi tests in Europe this year

-
 Trump meets new Syria leader after lifting sanctions
Trump meets new Syria leader after lifting sanctions
-
Equity markets swing as China-US trade euphoria fades

-
 Burberry warns 1,700 jobs at risk after annual loss
Burberry warns 1,700 jobs at risk after annual loss
-
Trump to meet new Syrian leader after offering sanctions relief

-
 'Children are innocent': Myanmar families in grief after school air strike
'Children are innocent': Myanmar families in grief after school air strike
-
Colombia joins Belt and Road initiative as China courts Latin America

-
 Australian champion cyclist Dennis gets suspended sentence after wife's road death
Australian champion cyclist Dennis gets suspended sentence after wife's road death
-
Protection racket? Asian semiconductor giants fear looming tariffs

-
 S. Korea Starbucks in a froth over presidential candidates names
S. Korea Starbucks in a froth over presidential candidates names
-
NATO hatches deal on higher spending to keep Trump happy

-
 Eurovision stage a dynamic 3D 'playground': producer
Eurovision stage a dynamic 3D 'playground': producer
-
Cruise unleashes 'Mission: Impossible' juggernaut at Cannes

-
 Suaalii in race to be fit for Lions Tests after fracturing jaw
Suaalii in race to be fit for Lions Tests after fracturing jaw
-
Pacers oust top-seeded Cavs, Nuggets on brink

-
 Sony girds for US tariffs after record annual net profit
Sony girds for US tariffs after record annual net profit
-
China, US slash sweeping tariffs in trade war climbdown

-
 Human Rights Watch warns of migrant worker deaths in 2034 World Cup host Saudi Arabia
Human Rights Watch warns of migrant worker deaths in 2034 World Cup host Saudi Arabia
-
Sony logs 18% annual net profit jump, forecast cautious

-
 China, US to lift sweeping tariffs in trade war climbdown
China, US to lift sweeping tariffs in trade war climbdown
-
Asian markets swing as China-US trade euphoria fades

-
 Australian seaweed farm tackles burps to help climate
Australian seaweed farm tackles burps to help climate
-
Judgment day in EU chief's Covid vaccine texts case


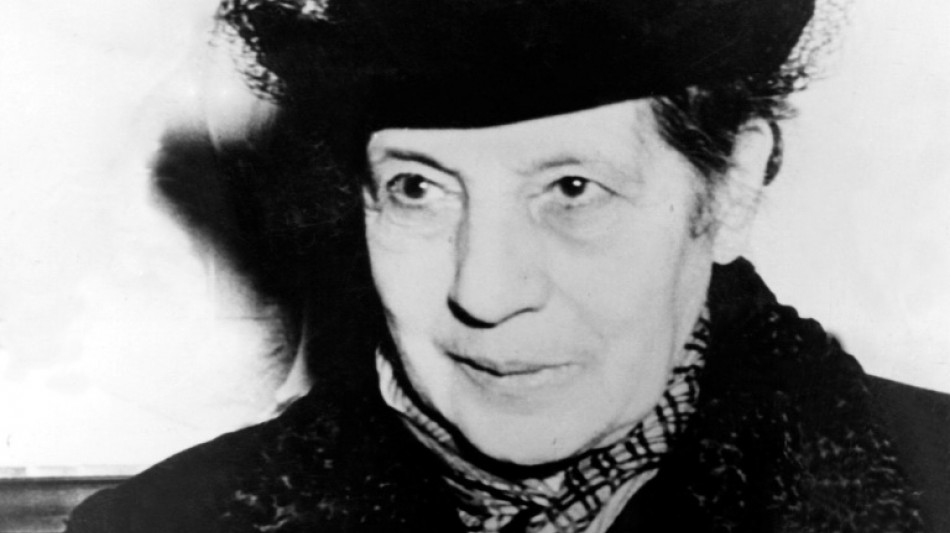
The women scientists forgotten by history
French doctor and researcher Marthe Gautier, who died over the weekend, was one of a long line of women scientists who greatly contributed to scientific discovery only to see the credit go to their male colleagues.
Here are just a few of the women scientists whose work was forgotten by history.
- Marthe Gautier -
Gautier, who died at the age of 96 on Saturday, discovered that people with Down's syndrome had an extra chromosome in 1958.
But when she was unable to identify the exact chromosome with her lower-power microscope, she "naively" lent her slides to geneticist Jerome Lejeune, she told the Science journal in 2014.
She was then "shocked" to see the discovery of the extra chromosome 21 published in research six month later, with Lejeune's name first and hers second -- and her name misspelled.
It was not until 1994 that the ethics committee of France's INSERM medical research institute said Lejeune was unlikely to have played the "dominant" role in the discovery.
- Rosalind Franklin -
British chemist Rosalind Franklin's experimental work led to her famous 1952 X-ray image "Photo 51", which helped unlock the discovery of the DNA double helix.
But Francis Crick and James Watson were working on a similar theory at the time, and their research was published ahead of Franklin's in the same journal, leading many to think her study merely supported theirs.
Crick and Watson won the Nobel Prize for Medicine for the discovery in 1962 -- Franklin had died four years earlier at the age of just 37.
In a letter from 1961 that emerged in 2013, Crick acknowledged the importance of her work in determining "certain features" of the molecule.
- Jocelyn Bell Burnell -
British astrophysicist Jocelyn Bell Burnell discovered the first radio pulsars when she was a postgraduate student in 1967.
But it was her thesis supervisor and another male astronomer who won 1974's Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery.
- Lise Meitner -
Austrian-Swedish physicist Lise Meitner was one of the key people responsible for discovering nuclear fission, leading to Albert Einstein dubbing her the "German Marie Curie".
However it was her long-term collaborator Otto Hahn who won the 1944 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery.
- Chien-Shiung Wu -
Chinese-American physicist Chien-Shiung Wu worked on the Manhattan Project and conducted the "Wu experiment", which overturned what had been previously considered a fundamental law of nature -- the conservation of parity.
But again it was her male colleagues who won the 1975 Nobel Physics prize for the research.
Her work earned her the nickname "Chinese Madame Curie".
- And so on -
The list could go -- and the women scientists named above are merely those whose contributions have been belatedly recognised decades later.
The contributions of male scientists' wives, mothers and daughters are also believed to have long been overlooked, including that of Einstein's first wife, mathematician and physicist Mileva Maric.
In 1993 American historian Margaret Rossiter dubbed the systematic suppression of women's contributions to scientific progress the "Matilda effect", after US rights activist Matilda Joslyn Gage.
Even today the role played by women in scientific history is under-represented in school textbooks, French historian Natalie Pigeard-Micault told AFP.
"It gives the impression that scientific research is limited to a handful of women," she said, pointing to how Marie Curie was always an "exceptional" reference point.
L.Durand--AMWN


