-
 Iran rocked by night of protests despite internet blackout: videos
Iran rocked by night of protests despite internet blackout: videos
-
Swiatek romps to United Cup victory in 58 minutes

-
 Procession of Christ's icon draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
Procession of Christ's icon draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
-
Every second counts for Japan's 'King Kazu' at 58

-
 Syria announces ceasefire with Kurdish fighters in Aleppo
Syria announces ceasefire with Kurdish fighters in Aleppo
-
Russia hits Ukraine with hypersonic missile after rejecting peacekeeping plan

-
 Asian stocks mixed ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
Asian stocks mixed ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
-
Scores without power as Storm Goretti pummels Europe

-
 Sabalenka gets revenge over Keys in repeat of Australian Open final
Sabalenka gets revenge over Keys in repeat of Australian Open final
-
Fresh from China, South Korea president to visit Japan

-
 Injured Kimmich to miss icy Bundesliga return for Bayern
Injured Kimmich to miss icy Bundesliga return for Bayern
-
Rybakina has little hope of change to tennis schedule

-
 Osimhen, Nigeria seek harmony with Algeria up next at AFCON
Osimhen, Nigeria seek harmony with Algeria up next at AFCON
-
US immigration agent's fatal shooting of woman leaves Minneapolis in shock

-
 After fire tragedy, small Swiss town mourns 'decimated generation'
After fire tragedy, small Swiss town mourns 'decimated generation'
-
Switzerland mourns Crans-Montana fire tragedy

-
 Russia bombards Kyiv after rejecting peacekeeping plan
Russia bombards Kyiv after rejecting peacekeeping plan
-
Crunch time for EU's long-stalled Mercosur trade deal

-
 Asian stocks rally ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
Asian stocks rally ahead of US jobs, Supreme Court ruling
-
'Sever the chain': scam tycoons in China's crosshairs

-
 Bulls-Heat NBA game postponed over 'moisture' on court
Bulls-Heat NBA game postponed over 'moisture' on court
-
Arsenal's Martinelli 'deeply sorry' for shoving injured Bradley

-
 Christ icon's procession draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
Christ icon's procession draws thousands to streets of Philippine capital
-
Moleiro shining as Villarreal make up La Liga ground after cup failures

-
 New Chelsea boss Rosenior faces FA Cup test
New Chelsea boss Rosenior faces FA Cup test
-
Vietnam shrugs off Trump tariffs as US exports surge

-
 Syrian government announces ceasefire in Aleppo after deadly clashes
Syrian government announces ceasefire in Aleppo after deadly clashes
-
New Zealand's rare flightless parrot begins breeding again

-
 Age no barrier for rampant Australia but future uncertain
Age no barrier for rampant Australia but future uncertain
-
Ex-delivery driver gives voice to China's precarious gig workers

-
 Protesters, US law enforcers clash after immigration agent kills woman
Protesters, US law enforcers clash after immigration agent kills woman
-
AI gobbling up memory chips essential to gadget makers

-
 'One Battle After Another' leads the charge for Golden Globes
'One Battle After Another' leads the charge for Golden Globes
-
Kyrgios to play doubles only at Australian Open

-
 Firefighters warn of 'hectic' Australian bushfires
Firefighters warn of 'hectic' Australian bushfires
-
International Space Station crew to return early after astronaut medical issue

-
 Arsenal in 'strong position' despite missed opportunity for Arteta
Arsenal in 'strong position' despite missed opportunity for Arteta
-
US House revolt advances Obamacare subsidy extension

-
 Swiss mining giant Glencore in merger talks with Rio Tinto
Swiss mining giant Glencore in merger talks with Rio Tinto
-
US snowboard star Kim dislocates shoulder ahead of Olympic three-peat bid

-
 Brazil's Lula vetoes bill reducing Bolsonaro's sentence
Brazil's Lula vetoes bill reducing Bolsonaro's sentence
-
AC Milan scrape a point with Genoa after late penalty howler

-
 Arsenal miss chance to stretch lead in Liverpool stalemate
Arsenal miss chance to stretch lead in Liverpool stalemate
-
Stocks mixed as traders await US jobs data, oil rebounds

-
 After Minneapolis shooting, AI fabrications of victim and shooter
After Minneapolis shooting, AI fabrications of victim and shooter
-
Trump says no pardon for Sean 'Diddy' Combs

-
 Venezuela begins 'large' prisoner release amid US pressure
Venezuela begins 'large' prisoner release amid US pressure
-
Real Madrid beat Atletico to set up Clasico Spanish Super Cup final

-
 Heavy wind, rain, snow batters Europe
Heavy wind, rain, snow batters Europe
-
PSG beat Marseille on penalties to win French Champions Trophy


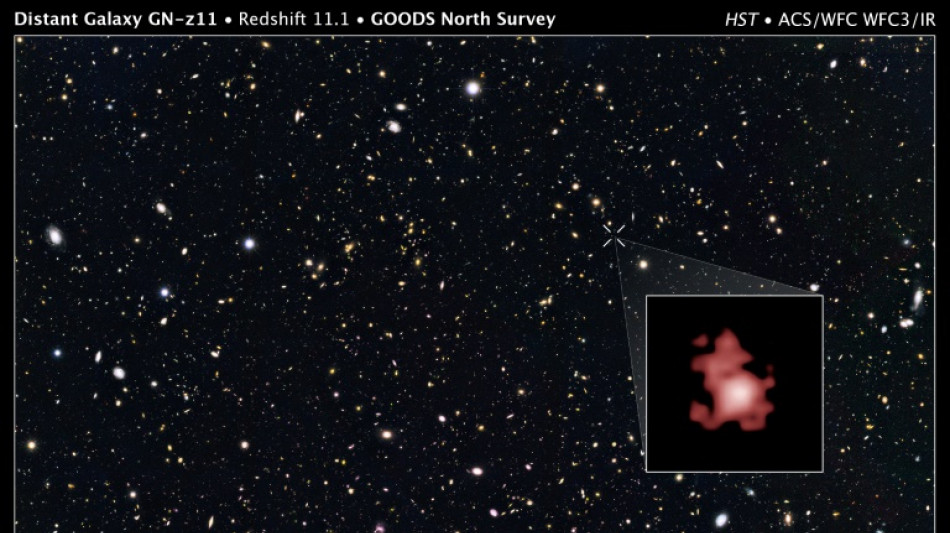
Webb telescope discovers oldest black hole yet
The James Webb space telescope has discovered the oldest black hole ever detected, which was thriving so soon after the Big Bang that it challenges our understanding of how these celestial behemoths form, astronomers said Wednesday.
The black hole was vigorously gobbling up its host galaxy just 430 million years after the birth of the universe during a period called the cosmic dawn, according to a study in the journal Nature.
That makes it 200 million years older than any other massive black hole ever observed, study co-author and Cambridge University astronomer Jan Scholtz told AFP.
Yet it has a mass 1.6 million times greater than our Sun.
Exactly how it had time to grow that big so quickly after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago will provide new information "for the next generation of theoretical models" aiming to explain what creates black holes, Scholtz said.
Like all black holes, it is invisible and can only be detected by the vast explosions of light created when it gobbles up whatever matter is unlucky enough to be nearby.
It was this light that allowed the Hubble space telescope in 2016 to spot its host galaxy GN-z11, which is in the direction of the Ursa Major constellation.
At the time GN-z11 was the oldest -- and therefore most distant -- galaxy ever observed. However Hubble did not spot the black hole lurking at its centre.
In 2022, Webb usurped Hubble as the most powerful space telescope, unleashing a torrent of discoveries that have scientists rushing to keep up.
Not only has it spotted the black hole at the heart of GN-z11, but it has also discovered galaxies even further back in time and space, which are also bigger than had been thought possible.
- Growing up fast -
The black hole was energetically eating up GN-z11 during the cosmic dawn, a period which came right after the universe's "dark ages," when stars and galaxies were first born.
It normally takes the supermassive black holes squatting at the centre of galaxies hundreds of millions -- if not billions -- of years to form.
So how could this one have grown so quickly?
Study co-author Stephane Charlot, an astrophysicist at France's Institut d'Astrophysique de Paris, suggested that black holes in the early universe could have been formed in a different way than those closer by.
One theory is that they were born huge due to the explosion of especially massive stars that only existed in the early universe, he told AFP.
Or they could have been created by the "direct collapse of a dense gas cloud, without going through the star formation phase," he added.
Once born, the black hole would have been able to gorge itself on the plentiful gas nearby, prompting an almighty growth spurt.
Scholtz emphasised that what has been discovered so far about the black hole of GN-z11 "doesn't rule out any of these scenarios".
And it could be just the beginning.
Scholtz hopes that Webb -- and other telescopes on the way, such as the European Space Agency's Euclid -- will discover more of these black holes in the earliest glimmers of the universe.
Y.Aukaiv--AMWN

