-
 Putin evokes WWII victory to rally Russia behind Ukraine offensive
Putin evokes WWII victory to rally Russia behind Ukraine offensive
-
China exports beat forecasts ahead of US tariff talks

-
 Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
-
Most stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal

-
 IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
-
German lender Commerzbank's profits jump as it fends off UniCredit

-
 Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
-
India says repulsed fresh Pakistan attacks as de-escalation efforts grow

-
 Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
-
'High expectations': EU looks to Merz for boost in tough times

-
 Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
-
China sales to US slump even as exports beat forecasts

-
 Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
-
Dethroned Bundesliga champions Leverkusen face uncertain future

-
 China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
-
French monuments in trouble while PSG prepare for Champions League final

-
 Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
-
Flick's Barca must show 'hunger' in crunch Liga Clasico

-
 Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
-
Timberwolves overpower Warriors to level series

-
 Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
-
Putin gears up to host world leaders at lavish army parade

-
 Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
-
Leo XIV, first US pope, to celebrate first mass as pontiff

-
 Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
-
Former head of crypto platform Celsius sentenced 12 years

-
 Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
-
Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Share Subscription, Director's Dealing and Update

-
 Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
-
'Great honor': world leaders welcome first US pope

-
 Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
-
Trump unveils UK trade deal, first since tariff blitz

-
 Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
-
Jeeno shines on greens to grab LPGA lead at Liberty National

-
 Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
-
AI tool uses selfies to predict biological age and cancer survival

-
 Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
-
Postecoglou hits back as Spurs reach Europa League final

-
 Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
-
Pope Leo XIV: Soft-spoken American spent decades amid poor in Peru

-
 First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
-
'Inexcusable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip

-
 US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
-
Stocks mostly rise as US-UK unveil trade deal

-
 Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
-
Anything but Europa League glory 'means nothing' for Man Utd: Amorim

-
 'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
-
Pope Leo 'fell in love with Peru'and ceviche: Peru bishop

-
 Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
-
India tells X to block over 8,000 accounts

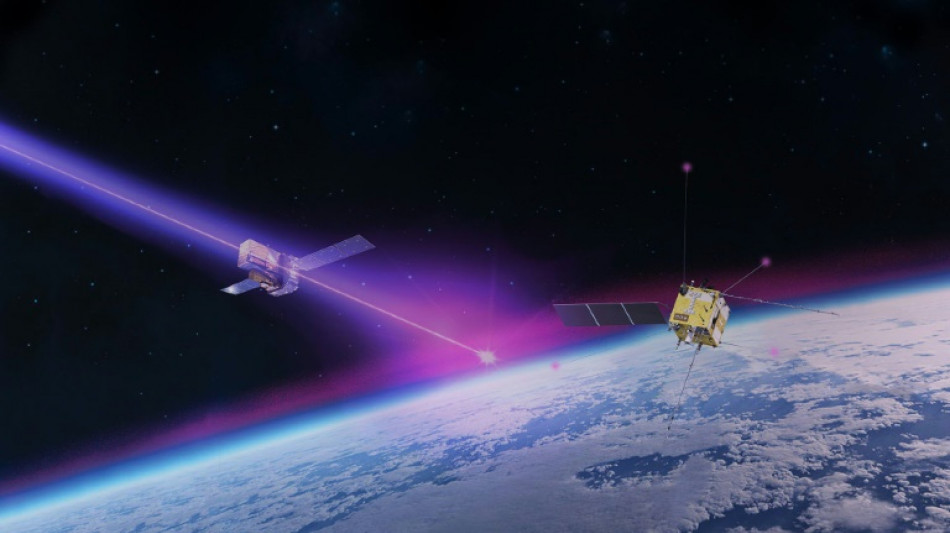
Brightest flash ever disturbed Earth's atmosphere last year
Last year the brightest flash of light ever seen in the night sky disturbed Earth's upper atmosphere in a way that has never before detected before, researchers said on Tuesday.
A massive burst of gamma rays from an enormous cosmic explosion around two billion light years away arrived at Earth on October 9, 2022, lighting up telescopes around the world.
Quickly nicknamed the "BOAT" -- for Brightest Of All Time -- the flash lasted just seven minutes but its afterglow was visible to amateur astronomers for seven hours.
The flash activated lightning detectors in India and triggered instruments that normally study explosions on the Sun called solar flares.
It also affected long wave radio communications in the lower ionosphere, a section of Earth's upper atmosphere around 60 to 350 kilometres (37 to 217 miles) above the surface.
The BOAT also affected the upper ionosphere -- the very first time a gamma-ray burst has been observed in this section of the atmosphere, a team of Italian and Chinese researchers said on Tuesday.
From 350 to 950 kilometres above Earth, near the edge of the space, the upper ionosphere is where radiation from the Sun turns into charged particles that form an important electric field.
Mirko Piersanti, a researcher at Italy's University of L'Aquila, told AFP that experts in this field had been debating for two decades whether gamma ray bursts could have any impact on the upper ionosphere.
"I think we finally answered the question," said Piersanti, the lead author of a new study in the journal Nature Communications.
The researchers were lucky that the Chinese–Italian CSES satellite, which has an electric field detector, "was exactly in the zone that was illuminated by the gamma-ray burst" 500 kilometres above Earth in the upper ionosphere, he said.
"We found a shape in the electric field that had never been observed before," Piersanti added.
"It is amazing," European Space Agency gamma-ray expert Erik Kuulkers said in a statement.
"We can see things that are happening in deep space but are also affecting Earth."
- Extinction threat? -
Piersanti said the research would help scientists understand the potential threat that other gamma-ray bursts could pose in the future.
The worst-case scenario would be if such a powerful blast came from much closer to home -- say, within our own Milky Way galaxy. That could "completely erase" Earth's ozone layer, he said.
This would expose everything on the surface to the full might of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation, potentially wiping out life on Earth.
There has previously been speculation that past gamma-ray bursts could have caused ancient mass extinction events.
But Piersanti emphasised that much remains unknown.
It is also possible that the ionosphere would absorb all the gamma rays and "nothing would happen" to those of us on the ground, he explained.
Last year's gamma-ray burst, officially called GRB 221009A, is believed to have been caused by either a massive dying star exploding into a supernova, or the birth of a black hole.
Given its immense power, it could also have been both -- a supernova explosion leading to the creation of a black hole.
The blast came from the direction of the constellation Sagitta and travelled an estimated 1.9 billion years to reach Earth.
It is now 2.4 billion light years away because of the expansion of the universe.
On average, more than one gamma-ray-burst reaches Earth every day.
But one with the brightness of the BOAT is estimated to come around once every 10,000 years.
F.Pedersen--AMWN