-
 Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
-
Most stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal

-
 IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
-
German lender Commerzbank's profits jump as it fends off UniCredit

-
 Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
-
India says repulsed fresh Pakistan attacks as de-escalation efforts grow

-
 Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
-
'High expectations': EU looks to Merz for boost in tough times

-
 Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
-
China sales to US slump even as exports beat forecasts

-
 Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
-
Dethroned Bundesliga champions Leverkusen face uncertain future

-
 China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
-
French monuments in trouble while PSG prepare for Champions League final

-
 Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
-
Flick's Barca must show 'hunger' in crunch Liga Clasico

-
 Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
-
Timberwolves overpower Warriors to level series

-
 Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
-
Putin gears up to host world leaders at lavish army parade

-
 Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
-
Leo XIV, first US pope, to celebrate first mass as pontiff

-
 Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
-
Former head of crypto platform Celsius sentenced 12 years

-
 Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
-
Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Share Subscription, Director's Dealing and Update

-
 Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
-
'Great honor': world leaders welcome first US pope

-
 Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
-
Trump unveils UK trade deal, first since tariff blitz

-
 Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
-
Jeeno shines on greens to grab LPGA lead at Liberty National

-
 Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
-
AI tool uses selfies to predict biological age and cancer survival

-
 Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
-
Postecoglou hits back as Spurs reach Europa League final

-
 Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
-
Pope Leo XIV: Soft-spoken American spent decades amid poor in Peru

-
 First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
-
'Inexcusable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip

-
 US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
-
Stocks mostly rise as US-UK unveil trade deal

-
 Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
-
Anything but Europa League glory 'means nothing' for Man Utd: Amorim

-
 'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
-
Pope Leo 'fell in love with Peru'and ceviche: Peru bishop

-
 Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
-
India tells X to block over 8,000 accounts
-
 Germany's Merz tells Trump US remains 'indispensable' friend
Germany's Merz tells Trump US remains 'indispensable' friend
-
Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her as a minor


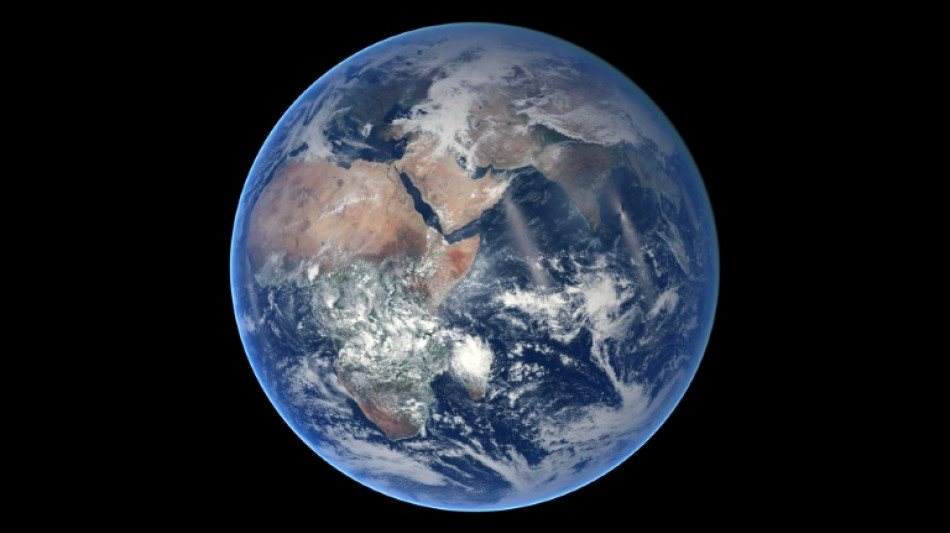
Huge 'blobs' inside Earth are from another planet, study suggests
Scientists proposed a novel idea on Wednesday that could solve two of the world's mysteries at once -- one that passes over our heads every night, and one that sits far below our feet.
The first mystery has puzzled everyone from scientists to inquisitive children for millennia: where did the Moon come from?
The leading theory is that the Moon was created 4.5 billion years ago when a would-be planet the size of Mars smashed into the still-forming Earth.
This epic collision between early Earth and the proto-planet called Theia shot an enormous amount of debris into orbit, which formed what would become the Moon.
Or so the theory goes. Despite decades of effort, scientists have not been able to find any evidence of Theia's existence.
New US-led research, published in the journal Nature, suggests they might have been looking in the wrong direction.
Around 2,900 kilometres (1,800 miles) below Earth's surface, two massive "blobs" have baffled geologists since seismic waves revealed their existence in the 1980s.
These continent-sized clumps of material straddle the bottom of Earth's rocky mantle near its molten core, one below Africa and the other underneath the Pacific Ocean.
Scientists have determined that the blobs are much hotter and more dense that the surrounding rock, but much else about them remains a mystery.
The new research on Wednesday indicates the blobs are "buried relics" of Theia that entered into Earth during their formative collision -- and have been hiding near our planet's heart ever since.
As well as creating the Moon, this collision and the remnants it left behind may have helped Earth become the unique life-hosting planet it is today, the researchers proposed.
- 'Very, very strange' -
Qian Yuan, a geodynamics researcher at the California Institute of Technology and the study's lead author, told AFP it is "very, very strange" that no evidence of the Theia impact has been found.
It was during a class held by a planetary scientist discussing this mystery that Yuan first connected the dots.
"Where is the impactor? My answer is: it's in the Earth," he said.
The planetary scientist holding the class had never heard of the blobs. The research has since required experts in the often separate fields of space and geology to join forces.
Yuan said that when Theia smashed into proto-Earth, it was travelling at more than 10 kilometres (six miles) a second, a speed that allowed some of it to penetrate "very deep into the Earth's lower mantle".
A video developed by the team simulating this process illustrates how clumps of Theia's mantle tens of kilometres wide swirled inside Earth.
As the mostly molten Theia material cooled and solidified, its high level of iron caused it to sink down to the border of Earth's mantle and core, the scientists proposed.
Over the years it accumulated into two separate blobs -- officially called large low-velocity provinces (LLVPs) -- that are now each larger than the Moon, Yuan said.
Testing a theory based so far back in time -- and so deep under Earth -- is incredibly difficult, and Yuan emphasised that their modelling could not be "100 percent" certain.
- 'Why Earth is unique' -
But if true, the implications could be immense.
Earth remains the only planet in the universe known to be capable of supporting life.
The Theia collision, which is believed to be Earth's last major accretion event, significantly changed its composition in just 24 hours, Yuan said.
"My feeling is that this initial condition is why Earth is unique -- why it's different to other rocky planets," he said.
Previous research has suggested that Theia could have brought water, the key ingredient of life, to Earth.
The blobs have been observed sending up "mantle plumes" -- columns of magma -- towards the Earth's surface, and have also been linked to the evolution of supercontinents.
Theia "left something in the Earth -- and that played a role in Earth's subsequent 4.5 billion years of evolution," Yuan said.
Christian Schroeder, an expert in both Earth science and planetary exploration at Scotland's University of Stirling, told AFP the theory "fits several strands of evidence".
"It is a very significant and exciting finding," said Schroeder, who was not involved in the research.
He emphasised that the mystery of the Moon's formation had not been solved.
But the research gives more weight to the Theia impact theory -- and provides "a credible explanation for these anomalies at the core-mantle boundary at the same time," he said.
The remnants of Theia potentially preserved underneath us "may be responsible for important processes on Earth ongoing to this day," Schroeder added.
H.E.Young--AMWN