
-
 Stocks drop after US economy contracts amid tariffs turmoil
Stocks drop after US economy contracts amid tariffs turmoil
-
US economy unexpectedly shrinks on import surge ahead of Trump tariffs

-
 Dravid says Suryavanshi, 14, needs support from fame
Dravid says Suryavanshi, 14, needs support from fame
-
Arsenal can win 'anywhere' says Merino after Champions League defeat by PSG

-
 Bangladesh crush Zimbabwe by an innings in second Test
Bangladesh crush Zimbabwe by an innings in second Test
-
Swiatek recovers against Keys to reach Madrid Open semis

-
 Spurs captain Son out of first leg of Europa League semi-final
Spurs captain Son out of first leg of Europa League semi-final
-
US economy unexpectedly shrinks in first three months of Trump presidency

-
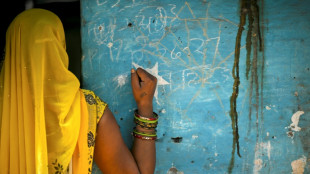 India to ask caste status in next census for first time in decades
India to ask caste status in next census for first time in decades
-
Burkina junta rallies supporters after claimed coup 'plot'

-
 Forest owner Marinakis steps back as European qualification looms
Forest owner Marinakis steps back as European qualification looms
-
US economy unexpectedly contracts in first three months of Trump presidency

-
 Bilbao will give 'soul' to beat Man United: Nico Williams
Bilbao will give 'soul' to beat Man United: Nico Williams
-
Sweden arrests teen after triple killing

-
 Pakistan says India planning strike after deadly Kashmir attack
Pakistan says India planning strike after deadly Kashmir attack
-
Cardinals lay groundwork for conclave, hope for quick vote

-
 More automakers drop earnings guidance over tariffs
More automakers drop earnings guidance over tariffs
-
William and Kate release romantic image on low-key anniversary

-
 Israel says strikes Syria to shield Druze as clashes spread
Israel says strikes Syria to shield Druze as clashes spread
-
Champions Cup format 'not perfect' says EPCR boss

-
 Iran hangs man as Israeli spy after 'unfair' trial: activists
Iran hangs man as Israeli spy after 'unfair' trial: activists
-
Stock markets mostly rise ahead of US economic data, tech earnings

-
 German growth better than expected but tariff turmoil looms
German growth better than expected but tariff turmoil looms
-
Sinner denies beneficial treatment in doping scandal ahead of Rome return

-
 Eurozone economy grows more than expected despite US tariff turmoil
Eurozone economy grows more than expected despite US tariff turmoil
-
Toulouse hooker Mauvaka out of Champions Cup semi

-
 Germany's next finance minister, 'bridge-builder' Lars Klingbeil
Germany's next finance minister, 'bridge-builder' Lars Klingbeil
-
Mehidy century puts Bangladesh in command against Zimbabwe

-
 Steelmaker ArcelorMittal warns of uncertainty
Steelmaker ArcelorMittal warns of uncertainty
-
Vietnam's Gen-Z captivated by 50-year-old military victory

-
 Moroccan-based cardinal says Church does not need Francis 'impersonator'
Moroccan-based cardinal says Church does not need Francis 'impersonator'
-
US official tells UN top court 'serious concerns' over UNRWA impartiality

-
 Jeep owner Stellantis suspends outlook over tariffs
Jeep owner Stellantis suspends outlook over tariffs
-
New Zealand, Phillippines sign troops deal in 'deteriorating' strategic environment

-
 Aston Martin limits US car imports due to tariffs
Aston Martin limits US car imports due to tariffs
-
Pakistan says India planning strike as tensions soar over Kashmir

-
 Australian triple-murder suspect allegedly cooked 'special' mushroom meal
Australian triple-murder suspect allegedly cooked 'special' mushroom meal
-
Most stock markets rise despite China data, eyes on US reports

-
 TotalEnergies profits drop as prices slide
TotalEnergies profits drop as prices slide
-
Volkswagen says tariffs will dampen business as profit plunges

-
 Jeep owner Stellantis suspends 2025 earnings forecast over tariffs
Jeep owner Stellantis suspends 2025 earnings forecast over tariffs
-
China's Shenzhou-19 astronauts return to Earth

-
 French economy returns to thin growth in first quarter
French economy returns to thin growth in first quarter
-
Ex-Premier League star Li Tie loses appeal in 20-year bribery sentence

-
 Belgium's green light for red light workers
Belgium's green light for red light workers
-
Haliburton leads comeback as Pacers advance, Celtics clinch

-
 Rahm out to break 2025 win drought ahead of US PGA Championship
Rahm out to break 2025 win drought ahead of US PGA Championship
-
Japan tariff envoy departs for round two of US talks

-
 Djurgarden eyeing Chelsea upset in historic Conference League semi-final
Djurgarden eyeing Chelsea upset in historic Conference League semi-final
-
Haliburton leads comeback as Pacers advance, Pistons stay alive

| RYCEF | -1.28% | 10.12 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.32% | 22.17 | $ | |
| RELX | 0% | 53.79 | $ | |
| BCC | -3.42% | 91.375 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.7% | 21.768 | $ | |
| SCS | -2.88% | 9.73 | $ | |
| RBGPF | -0.71% | 63 | $ | |
| NGG | -0.56% | 72.635 | $ | |
| RIO | -3.64% | 58.74 | $ | |
| GSK | 2.62% | 40.02 | $ | |
| CMSD | -0.68% | 22.2 | $ | |
| VOD | 0.73% | 9.65 | $ | |
| JRI | -1.86% | 12.694 | $ | |
| AZN | 0.01% | 71.715 | $ | |
| BP | -1.08% | 27.77 | $ | |
| BTI | 1.51% | 43.515 | $ |

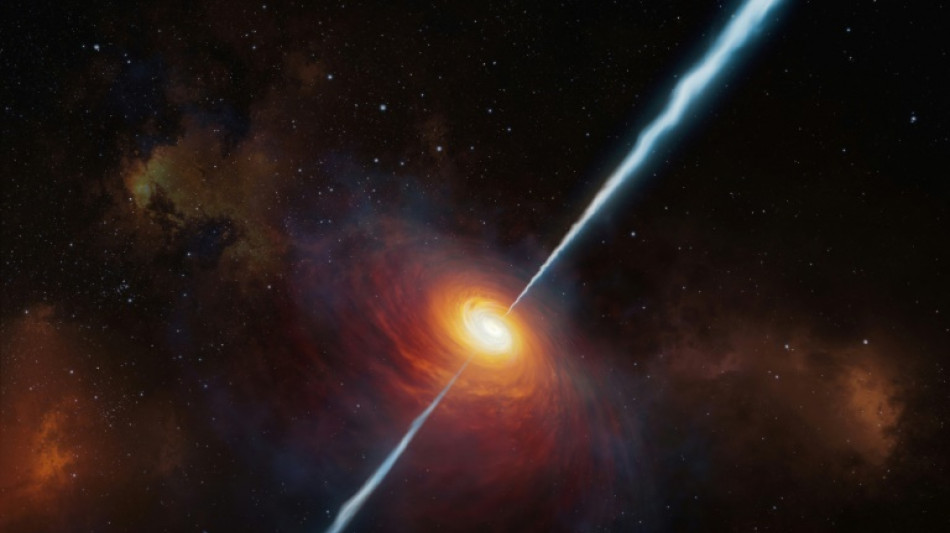
Time appears five times slower in early universe: study
Time appears to run five times slower in the early universe, scientists said on Monday, for the first time using extraordinarily bright cosmic objects called quasars as "clocks" to confirm this strange phenomenon.
Einstein's theory of relativity predicts that because space is expanding, "we should see the distant universe run in slow motion," said Geraint Lewis, an astrophysicist at the University of Sydney and the lead author of a new study.
Researchers had previously used observations of very bright exploding stars called supernovas as cosmic clocks to show that time ran twice as slowly back when the universe was half its current age.
The new study used even brighter quasars to peer further back into the history of the 13.8-billion-year-old universe.
Just over a billion years after the Big Bang, time appeared to flow five times slower, according to the study in the journal Nature Astronomy.
While "everything looks like it's slowed down" from here, Lewis emphasised that the experience of time in these distant places was not different.
"If I could magically transport you back 10 billion years and drop you next to one of these quasars, and you've got a stopwatch, time would just be normal," he told AFP.
"One second would be one second."
- Cosmic clocks -
Aiming to measure this phenomenon, which is called cosmological time dilation, Lewis and University of Auckland statistician Brendon Brewer analysed data from 190 quasars collected over two decades.
Quasars -- supermassive black holes at the centres of distant galaxies -- are thought to be the brightest and most powerful objects in the universe.
This makes them "useful beacons for charting the universe," Lewis said.
But they have proved more difficult to turn into cosmic clocks than supernovas, which provide a reliable single flash as a "tick".
Previous attempts to use quasars to measure time dilation had failed, leading to some "strange suggestions," Lewis said.
These included theories that perhaps quasars were not as distant as had been thought -- or even that "something fundamental was broken" in cosmology, he said.
But the new research "puts everything back in the right place," Lewis said.
It also confirmed that "Einstein is right again," he added.
The researchers were able to succeed where other attempts had fallen short because they had far more data on quasars, according to Lewis. Recent advances in the statistical understanding of randomness also helped.
To turn quasars into clocks with measurable ticks, the researchers had to make sense of the turbulent explosions that occurred as the black holes swallowed material.
Lewis compared it to watching a fireworks display, in which the great flashes seem random but different elements are "brightening and fading on their own kind of timescales".
"What we have done is unravel this firework display, showing that quasars, too, can be used as standard markers of time for the early universe."
F.Bennett--AMWN


