-
 Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
-
Most stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal

-
 IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
-
German lender Commerzbank's profits jump as it fends off UniCredit

-
 Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
-
India says repulsed fresh Pakistan attacks as de-escalation efforts grow

-
 Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
-
'High expectations': EU looks to Merz for boost in tough times

-
 Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
-
China sales to US slump even as exports beat forecasts

-
 Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
-
Dethroned Bundesliga champions Leverkusen face uncertain future

-
 China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
-
French monuments in trouble while PSG prepare for Champions League final

-
 Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
-
Flick's Barca must show 'hunger' in crunch Liga Clasico

-
 Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
-
Timberwolves overpower Warriors to level series

-
 Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
-
Putin gears up to host world leaders at lavish army parade

-
 Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
-
Leo XIV, first US pope, to celebrate first mass as pontiff

-
 Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
-
Former head of crypto platform Celsius sentenced 12 years

-
 Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
-
Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Share Subscription, Director's Dealing and Update

-
 Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
-
'Great honor': world leaders welcome first US pope

-
 Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
-
Trump unveils UK trade deal, first since tariff blitz

-
 Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
-
Jeeno shines on greens to grab LPGA lead at Liberty National

-
 Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
-
AI tool uses selfies to predict biological age and cancer survival

-
 Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
-
Postecoglou hits back as Spurs reach Europa League final

-
 Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
-
Pope Leo XIV: Soft-spoken American spent decades amid poor in Peru

-
 First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
-
'Inexcusable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip

-
 US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
-
Stocks mostly rise as US-UK unveil trade deal

-
 Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
-
Anything but Europa League glory 'means nothing' for Man Utd: Amorim

-
 'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
-
Pope Leo 'fell in love with Peru'and ceviche: Peru bishop

-
 Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
-
India tells X to block over 8,000 accounts
-
 Germany's Merz tells Trump US remains 'indispensable' friend
Germany's Merz tells Trump US remains 'indispensable' friend
-
Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her as a minor


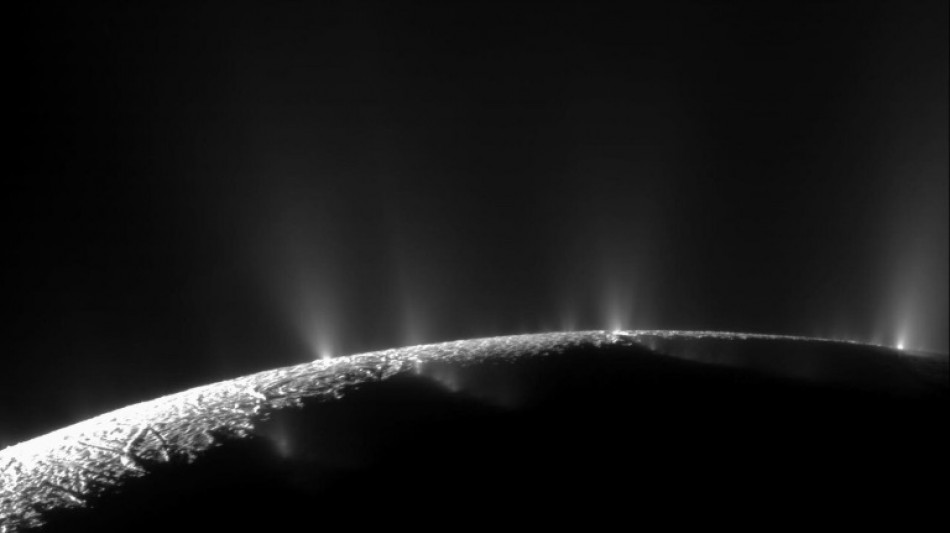
NASA finds key building block for life in a moon of Saturn
The long hunt for extraterrestrials just got a big boost.
Scientists have discovered that phosphorus, a key building block of life, lies in the ocean beneath the icy surface of Saturn's moon Enceladus.
The finding was based on a review of data collected by NASA's Cassini probe, and was published Wednesday in the prestigious journal Nature.
Cassini started exploring Saturn and its rings and moons in 2004, before burning up in the gas giant's atmosphere when its mission ended in 2017.
"This is a stunning discovery for astrobiology," said Christopher Glein of the Southwest Research Institute, one of the paper's co-authors, adding: "We have found abundant phosphorus in plume ice samples spraying out of the subsurface ocean."
Geysers on Enceladus' south pole spew icy particles through cracks on the surface out into space, feeding Saturn's E ring -- the faint ring outside the brighter main rings.
Scientists previously found other minerals and organic compounds in the ejected ice grains, but not phosphorus, which is an essential building block for DNA and RNA, and is also found in the bones and teeth of people, animals, and even ocean plankton.
Simply put, life as we know it would not be possible without phosphorus.
While geochemical modeling had previously found it was likely phosphorus would also be present, and this prediction was published in an earlier paper, it is one thing to forecast something and another to confirm, said Glein.
"It's the first time this essential element has been discovered in an ocean beyond Earth," added first author Frank Postberg, a planetary scientist at Freie Universitat Berlin, in a NASA statement.
To make the new discovery, authors combed through data collected by Cassini's Cosmic Dust Analyzer instrument, and confirmed the findings by carrying out laboratory experiments to show that Enceladus' ocean has phosphorus bound inside different water-soluble forms.
Over the past 25 years, planetary scientists have discovered that worlds with oceans beneath a surface layer of ice are common in our solar system.
These include Jupiter's moon Europa, Saturn's largest moon Titan, but even the more distant body, Pluto.
While planets like Earth that have surface oceans need to reside within a narrow window of distance from their host star to maintain the right temperatures for life, the discovery of worlds with subsurface oceans expands the number of habitable bodies that might exist.
"With this finding, the ocean of Enceladus is now known to satisfy what is generally considered to be the strictest requirement for life," said Glein.
"The next step is clear –- we need to go back to Enceladus to see if the habitable ocean is actually inhabited."
L.Durand--AMWN