-
 UK economy slows, hitting government growth plans
UK economy slows, hitting government growth plans
-
Primary schools empty as smog persists in Indian capital

-
 Palestinians turn to local soda in boycott of Israel-linked goods
Palestinians turn to local soda in boycott of Israel-linked goods
-
Typhoon Man-yi bears down on Philippines still reeling from Usagi

-
 UK growth slows in third quarter, dealing blow to Labour government
UK growth slows in third quarter, dealing blow to Labour government
-
Chris Wood hits quickfire double in NZ World Cup qualifying romp

-
 Markets struggle at end of tough week
Markets struggle at end of tough week
-
China tests building Moon base with lunar soil bricks

-
 Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival
Film's 'search for Palestine' takes centre stage at Cairo festival
-
Oil execs work COP29 as NGOs slam lobbyist presence

-
 Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
Gore says climate progress 'won't slow much' because of Trump
-
'Megaquake' warning hits Japan's growth

-
 Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
Stiff business: Berlin startup will freeze your corpse for monthly fee
-
Wars, looming Trump reign set to dominate G20 summit

-
 Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet
Xi, Biden attend Asia-Pacific summit, prepare to meet
-
Kyrgios to make competitive return at Brisbane next month after injuries

-
 Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys
Dominican Juan Luis Guerra triumphs at 25th annual Latin Grammys
-
Landslide win for Sri Lanka president's leftist coalition in snap polls

-
 Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break
Australian World Cup penalty hero Vine takes mental health break
-
As Philippines picks up from Usagi, a fresh storm bears down

-
 Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
Tropical Storm Sara pounds Honduras with heavy rain
-
Pepi gives Pochettino win for USA in Jamaica

-
 'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner
'Hell to heaven' as China reignite World Cup hopes with late winner
-
Rebel attacks keep Indian-run Kashmir on the boil

-
 New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France
New Zealand challenge 'immense but fantastic' for France
-
Under pressure England boss Borthwick in Springboks' spotlight

-
 All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown
All Blacks plan to nullify 'freakish' Dupont, says Lienert-Brown
-
TikTok makes AI driven ad tool available globally

-
 Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
Japan growth slows as new PM readies stimulus
-
China retail sales pick up speed, beat forecasts in October

-
 Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week
Asian markets fluctuate at end of tough week
-
Gay, trans people voicing -- and sometimes screaming -- Trump concerns

-
 Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela
Argentina fall in Paraguay, Brazil held in Venezuela
-
N. Korean leader orders 'mass production' of attack drones

-
 Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
Pakistan's policies hazy as it fights smog
-
Nature pays price for war in Israel's north

-
 New Zealand's prolific Williamson back for England Test series
New Zealand's prolific Williamson back for England Test series
-
Mexico City youth grapple with growing housing crisis

-
 After Trump's victory, US election falsehoods shift left
After Trump's victory, US election falsehoods shift left
-
Cracks deepen in Canada's pro-immigration 'consensus'

-
 Xi inaugurates South America's first Chinese-funded port in Peru
Xi inaugurates South America's first Chinese-funded port in Peru
-
Tyson slaps Paul in final face-off before Netflix bout

-
 England wrap-up T20 series win over West Indies
England wrap-up T20 series win over West Indies
-
Stewards intervene to stop Israel, France football fans clash at Paris match

-
 Special counsel hits pause on Trump documents case
Special counsel hits pause on Trump documents case
-
Japan's Princess Mikasa, great aunt to emperor, dies aged 101

-
 Cricket at 2028 Olympics could be held outside Los Angeles
Cricket at 2028 Olympics could be held outside Los Angeles
-
Trump names vaccine skeptic RFK Jr. to head health dept

-
 Ye claims 'Jews' controlling Kardashian clan: lawsuit
Ye claims 'Jews' controlling Kardashian clan: lawsuit
-
Japan into BJK Cup quarter-finals as Slovakia stun USA

| CMSD | -0.02% | 24.725 | $ | |
| SCS | -0.75% | 13.27 | $ | |
| BP | 1.65% | 29.05 | $ | |
| GSK | -2.09% | 34.39 | $ | |
| JRI | -0.23% | 13.21 | $ | |
| CMSC | -0.24% | 24.55 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 100% | 61.84 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.57% | 140.35 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.2% | 35.49 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.4% | 62.37 | $ | |
| RIO | -0.31% | 60.43 | $ | |
| RYCEF | -4.71% | 6.79 | $ | |
| BCE | -1.38% | 26.84 | $ | |
| AZN | -0.38% | 65.04 | $ | |
| VOD | -0.81% | 8.68 | $ | |
| RELX | -0.37% | 45.95 | $ |

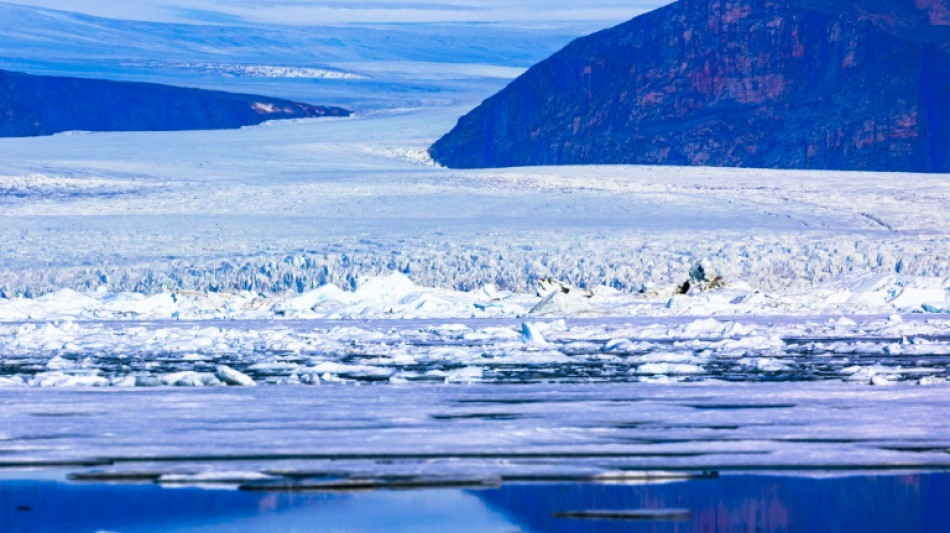
'Snowball Earth' might have been rather slushy: study
Millions of years ago, the Earth was so cold that most of its surface was covered in ice. But that hard freeze might have been slushier than once thought.
The longstanding "Snowball Earth" theory imagines our world as seen from space, a perfect sphere with ice covering land and sea alike.
It draws on clues including deposits made by glaciers near the Equator. For ice to have extended that far from the poles suggests much of our planet was once frozen.
But there has long been speculation about just how complete the cover was, with some convinced that areas of slush or open ocean remained, allowing oxygen to penetrate and creating incubators for life.
New research published Tuesday in the journal Nature Communications adds weight to that theory, and suggests these oases in the tundra might have existed much further north than previously suspected.
The evidence comes from a thin layer of black shale that would have been under the sea during the Marinoan ice age, which began around 650 million years ago.
The shale in the Nantuo Formation in southern China acts as a sort of archive for the conditions in oceans at the time.
By analysing levels of elements such as iron, and the presence of nitrogen, scientists can infer whether oxygen was penetrating the ocean and nitrogen was being produced by lifeforms.
"We found evidence of ice-free conditions at mid-northern paleolatitudes (locations before continental drift)," Huyue Song, who helped lead the research, told AFP.
"Until now, ice-free areas had been identified only in peri-equatorial regions."
Instead of a "narrow ice-free belt" across the middle of the Earth, "patchy ice-free areas may have existed much more widely," added Song, a professor at the China University of Geosciences, Wuhan.
The findings build on other research at sites ranging from Australia to Brazil that suggest life was able to cling on in pockets while most of Earth was in deep freeze.
These incubators may even have helped spur "a rapid rebound of the biosphere" at the end of the ice age, the research published Tuesday argues.
The work took four years in total, and involved collecting samples at a remote site in the Shennongjia region of Hubei province, some 500 kilometres from Song's base in Wuhan.
Song believes the findings will help scientists better understand both how our planet's climate works, and how life evolved and survived on Earth through the ages.
And while Earth's ice ages might seem like ancient history, Song argues they could have useful lessons for a planet now experiencing new severe climate change.
"It provides insight into how life survived extreme climate events -- a topic that will become of increasing relevance as modern climate change intensifies," he said.
F.Pedersen--AMWN