
-
 Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?
Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?
-
WHO pandemic agreement talks face deadline crunch
-
 Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns
Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns
-
LeMond hails 'one in a million' Pogacar ahead of Paris-Roubaix debut

-
 Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts
Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts
-
Trump admits trade war 'cost' as markets hit

-
 AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game
AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game
-
Despite Trump pause, overall US tariff rate at highest in a century

-
 'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims
'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims
-
Panama deal allows US to deploy troops to canal

-
 US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves
US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves
-
Grieving Dominicans start burying 220 victims of nightclub disaster

-
 Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National
Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National
-
US auto union praises some Trump tariffs

-
 Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
-
Rose: I've played well enough to win Masters but lack the jacket

-
 Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead
Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead
-
Rose rockets to Masters lead, defending champ Scheffler in pursuit

-
 Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi
Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi
-
Oscars to add new award for stunts

-
 Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'
Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'
-
'Mistakes can happen': Amorim backs Onana after Lyon nightmare

-
 RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'
RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'
-
Tourist family, pilot killed in 'tragic' NY helicopter crash

-
 No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title
No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title
-
Man Utd and Spurs draw in Europa League, Rangers hold Athletic

-
 Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit
Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit
-
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors in Europa League

-
 Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors
-
Wall Street rally fizzles as tariff fears resurface

-
 MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study
MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study
-
Argentina braves 24-hour strike as it awaits word on IMF loan

-
 Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard
Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard
-
Porro rescues Postecoglou as Spurs held by Frankfurt

-
 Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster
Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster
-
CONMEBOL proposes one-off 64-team World Cup in 2030

-
 Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup
Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup
-
Former Real Madrid coach Leo Beenhakker dies aged 82

-
 Rose rockets to top of Masters leaderboard, Scheffler one back
Rose rockets to top of Masters leaderboard, Scheffler one back
-
Langer fades after fiery start in Masters farewell

-
 Iran, US raise stakes ahead of key talks in Oman
Iran, US raise stakes ahead of key talks in Oman
-
US-China confrontation overshadows Trump's 'beautiful' trade war

-
 RFK, MLK assassination files to be released in 'next few days'
RFK, MLK assassination files to be released in 'next few days'
-
Relevent settle anti-trust lawsuit with US Soccer

-
 Orcas, dolphins stuck in closed French marine park
Orcas, dolphins stuck in closed French marine park
-
Rahul shines as Delhi bag fourth straight win in IPL

-
 Family bid farewell to merengue singer, killed in Dominican nightclub disaster
Family bid farewell to merengue singer, killed in Dominican nightclub disaster
-
Mbappe ups stakes in bid to recoup 55mn euros from PSG

-
 Scheffler grabs share of early lead in quest for Masters repeat
Scheffler grabs share of early lead in quest for Masters repeat
-
Why did a Dominican nightclub roof cave in?


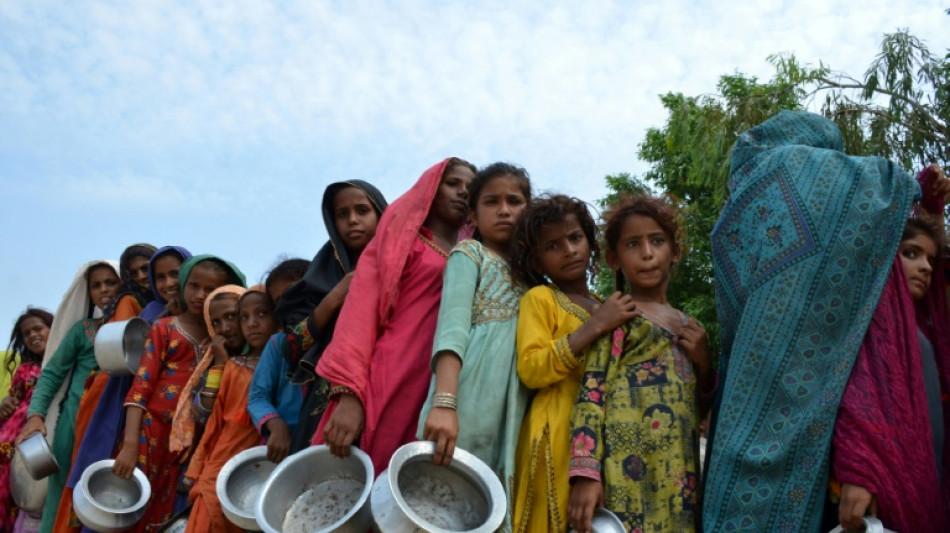
Climate-fueled hunger more than doubles in worst-hit countries: report
From record droughts to catastrophic floods, the world's worst climate hotspots are seeing a surge in acute hunger, according to an Oxfam report that called on rich nations to drastically cut their emissions and compensate low-income countries.
The analysis, "Hunger in a heating world," found that acute hunger had risen 123 percent over six years in the ten most-affected nations, defined by the most number of UN weather appeals.
"The effects of severe weather events are already being felt," Lia Lindsey, Oxfam America's senior humanitarian policy advisory told AFP, adding the report was timed to pressure world leaders at the UN General Assembly to act.
The countries -- Somalia, Haiti, Djibouti, Kenya, Niger, Afghanistan, Guatemala, Madagascar, Burkina Faso and Zimbabwe -- have repeatedly been battered by extreme weather over the last two decades.
An estimated 48 million people across those countries suffer acute hunger, defined as hunger resulting from a shock and causing risks to lives and livelihoods and based on reports compiled by the World Food Programme.
That figure is up from 21 million people in 2016; 18 million people are on the brink of starvation.
The report acknowledges the complexity surrounding the causes of global hunger, with conflict and economic disruption -- including those from the Covid-19 pandemic -- remaining key drivers.
"However, these new and worsening weather extremes are increasingly peeling away the abilities of poor people particularly in low-income countries to stave off hunger and cope with the next shock," it said.
Somalia, for example, is facing its worst drought on record, forcing one million people to flee their homes.
Climate change is also causing more frequent and intense heat waves and other extreme weather including floods, which covered one-third of Pakistan, washing away crops and topsoil and destroying farming infrastructure.
In Guatemala, weather conditions have contributed to the loss of close to 80 percent of the maize harvest, as well as causing a "coffee crisis" in the region that has hit vulnerable communities hardest and forced many to migrate to the United States.
- 'Obligation, not charity' -
Oxfam stressed that climate-fueled hunger is a "stark demonstration of global inequality," with the countries least responsible for the crisis suffering most from its impact.
Polluting industrialized nations such as those of the G20 are responsible for more than three-quarters of the world's carbon emissions, while the 10 climate hotspots are collectively responsible for just 0.13 percent.
"Leaders especially of rich polluting countries must live up to their promises to cut emissions," said Gabriela Bucher, Oxfam International executive director, in a statement.
"They must pay for adaptation measures and loss-and-damage in low-income countries, as well as immediately inject lifesaving funds to meet the UN appeal to respond to the most impacted countries."
The UN humanitarian appeal for 2022 comes to $49 billion, which Oxfam noted was equivalent to less than 18 days of profit for fossil fuel companies, when looking at average daily profits over the last 50 years.
Canceling debt can also help governments free up resources, said Bucher, with rich countries holding a moral responsibility to compensate poorer, most-affected countries.
"This is an ethical obligation, not charity," she said.
P.Mathewson--AMWN


