
-
 Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?
Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?
-
WHO pandemic agreement talks face deadline crunch
-
 Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns
Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns
-
LeMond hails 'one in a million' Pogacar ahead of Paris-Roubaix debut

-
 Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts
Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts
-
Trump admits trade war 'cost' as markets hit

-
 AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game
AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game
-
Despite Trump pause, overall US tariff rate at highest in a century

-
 'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims
'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims
-
Panama deal allows US to deploy troops to canal

-
 US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves
US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves
-
Grieving Dominicans start burying 220 victims of nightclub disaster

-
 Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National
Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National
-
US auto union praises some Trump tariffs

-
 Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
-
Rose: I've played well enough to win Masters but lack the jacket

-
 Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead
Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead
-
Rose rockets to Masters lead, defending champ Scheffler in pursuit

-
 Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi
Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi
-
Oscars to add new award for stunts

-
 Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'
Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'
-
'Mistakes can happen': Amorim backs Onana after Lyon nightmare

-
 RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'
RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'
-
Tourist family, pilot killed in 'tragic' NY helicopter crash

-
 No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title
No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title
-
Man Utd and Spurs draw in Europa League, Rangers hold Athletic

-
 Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit
Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit
-
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors in Europa League

-
 Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors
-
Wall Street rally fizzles as tariff fears resurface

-
 MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study
MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study
-
Argentina braves 24-hour strike as it awaits word on IMF loan

-
 Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard
Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard
-
Porro rescues Postecoglou as Spurs held by Frankfurt

-
 Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster
Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster
-
CONMEBOL proposes one-off 64-team World Cup in 2030

-
 Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup
Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup
-
Former Real Madrid coach Leo Beenhakker dies aged 82

-
 Rose rockets to top of Masters leaderboard, Scheffler one back
Rose rockets to top of Masters leaderboard, Scheffler one back
-
Langer fades after fiery start in Masters farewell

-
 Iran, US raise stakes ahead of key talks in Oman
Iran, US raise stakes ahead of key talks in Oman
-
US-China confrontation overshadows Trump's 'beautiful' trade war

-
 RFK, MLK assassination files to be released in 'next few days'
RFK, MLK assassination files to be released in 'next few days'
-
Relevent settle anti-trust lawsuit with US Soccer

-
 Orcas, dolphins stuck in closed French marine park
Orcas, dolphins stuck in closed French marine park
-
Rahul shines as Delhi bag fourth straight win in IPL

-
 Family bid farewell to merengue singer, killed in Dominican nightclub disaster
Family bid farewell to merengue singer, killed in Dominican nightclub disaster
-
Mbappe ups stakes in bid to recoup 55mn euros from PSG

-
 Scheffler grabs share of early lead in quest for Masters repeat
Scheffler grabs share of early lead in quest for Masters repeat
-
Why did a Dominican nightclub roof cave in?


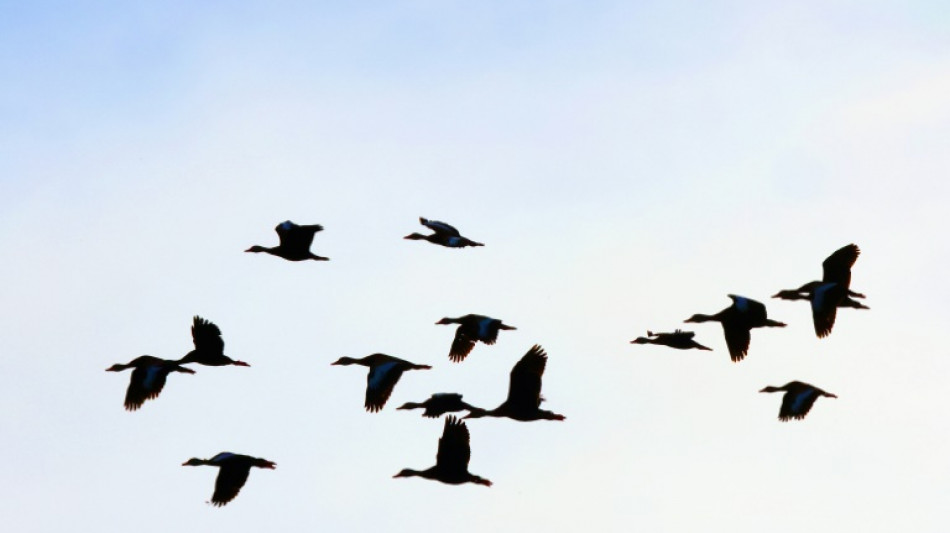
Mercury pollution makes ducks more likely to get bird flu: study
Ducks contaminated by mercury pollution are significantly more likely to get bird flu, a study found Wednesday, pointing towards another way that human-driven changes to the natural world increase the risk of viruses spreading.
Bird flu rarely infects humans but persistent outbreaks in the US and UK among other countries have led to millions of poultry being culled so far this year.
Wild waterfowl such as ducks are believed to be superspreaders of the virus in part because they travel so far as they migrate, potentially infecting other birds along the way.
For the new study, scientists shot down nearly 750 wild ducks from 11 different species in California's San Francisco Bay, which is in a migratory path that stretches from Alaska to Patagonia.
They then tested the ducks for mercury contamination and whether they were infected with bird flu -- or had antibodies for the virus in their system.
The results, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, showed that ducks contaminated with mercury were up to 3.5 times more likely to have had bird flu at some point over the last year or so.
The study's lead author, Claire Teitelbaum, a quantitative ecologist at the USGS Eastern Ecological Science Center, said mercury contamination "can suppress the immune system, and that might make infection with anything -- including influenza -- more likely".
The San Francisco Bay is also a "significant hotspot for mercury contamination in North America... largely from historical gold mining, where mercury was part of that process," she told AFP.
The ducks however tested negative to the highly pathogenic H5N1 bird flu strain that has been detected in many parts of the world.
- More bird flu likely -
Teitelbaum said that bird flu outbreaks in the United States had slowed down during the summer "because many of the wild birds are up on their breeding grounds" farther north.
But "as they're starting to come back down, we're probably going to see a lot more activity", she warned.
The spread comes as researchers increasingly sound the alarm that climate change, deforestation, livestock farming and other human-induced factors raise the likelihood of viruses crossing over from animals to humans.
Teitelbaum said that "there are just so many ways in which humans have historically altered and are continuing to alter the natural environment."
How pollution and contamination affect the risk of diseases spreading is "just another link that we need to add in to our more holistic view of what's going on in the world," she said.
Daniel Becker, a biologist at the University of Oklahoma not involved in the research, hailed the "impressive" study.
"There is surprisingly little work looking at contaminant concentrations in wildlife and their relationship to infectious disease," especially for viruses that can cross over to humans like bird flu, he said.
A.Rodriguezv--AMWN


