
-
 Saka 'ready to go' after long injury lay-off: Arteta
Saka 'ready to go' after long injury lay-off: Arteta
-
Ingebrigtsen Sr, on trial for abusing Olympic champion, says he was 'overly protective'

-
 Tourists and locals enjoy 'ephemeral' Tokyo cherry blossoms
Tourists and locals enjoy 'ephemeral' Tokyo cherry blossoms
-
Khamenei warns of 'strong' response if Iran attacked

-
 France fines Apple 150 million euros over privacy feature
France fines Apple 150 million euros over privacy feature
-
UK PM urges nations to smash migrant smuggling gangs 'once and for all'

-
 Thai authorities probe collapse at quake-hit construction site
Thai authorities probe collapse at quake-hit construction site
-
France's Le Pen convicted in fake jobs trial

-
 Chinese tech giant Huawei says profits fell 28% last year
Chinese tech giant Huawei says profits fell 28% last year
-
Trump says confident of TikTok deal before deadline
-
 Myanmar declares week of mourning as hopes fade for quake survivors
Myanmar declares week of mourning as hopes fade for quake survivors
-
Japan's Nikkei leads hefty market losses, gold hits record

-
 Tears in Taiwan for relatives hit by Myanmar quake
Tears in Taiwan for relatives hit by Myanmar quake
-
Venezuela says US revoked transnational oil, gas company licenses

-
 'Devastated': Relatives await news from Bangkok building collapse
'Devastated': Relatives await news from Bangkok building collapse
-
Arsenal, Tottenham to play pre-season North London derby in Hong Kong

-
 Japan's Nikkei leads hefty equity market losses; gold hits record
Japan's Nikkei leads hefty equity market losses; gold hits record
-
Israel's Netanyahu picks new security chief, defying legal challenge

-
 Trump says US tariffs to hit 'all countries'
Trump says US tariffs to hit 'all countries'
-
Prayers and tears for Eid in quake-hit Mandalay

-
 After flops, movie industry targets fresh start at CinemaCon
After flops, movie industry targets fresh start at CinemaCon
-
Tsunoda targets podium finish in Japan after 'unreal' Red Bull move

-
 French chefs await new Michelin guide
French chefs await new Michelin guide
-
UK imposes travel permit on Europeans from Wednesday

-
 At his academy, Romanian legend Hagi shapes future champions
At his academy, Romanian legend Hagi shapes future champions
-
Referee's lunch break saved Miami winner Mensik from early exit

-
 Djokovic refuses to discuss eye ailment after shock Miami loss
Djokovic refuses to discuss eye ailment after shock Miami loss
-
Mitchell magic as Cavs bag 60th win, Pistons and T'Wolves brawl

-
 Mensik shocks Djokovic to win Miami Open
Mensik shocks Djokovic to win Miami Open
-
Duterte lawyer: 'compelling' grounds to throw case out

-
 What happens on Trump's 'Liberation Day' and beyond?
What happens on Trump's 'Liberation Day' and beyond?
-
Clock ticks on Trump's reciprocal tariffs as countries seek reprieve

-
 Japan-Australia flagship hydrogen project stumbles
Japan-Australia flagship hydrogen project stumbles
-
Musk deploys wealth in bid to swing Wisconsin court vote

-
 Mensik upsets Djokovic to win Miami Open
Mensik upsets Djokovic to win Miami Open
-
China manufacturing activity grows at highest rate in a year

-
 'Waited for death': Ex-detainees recount horrors of Sudan's RSF prisons
'Waited for death': Ex-detainees recount horrors of Sudan's RSF prisons
-
Japan's Nikkei leads big losses in Asian markets as gold hits record

-
 Rescue hopes fading three days after deadly Myanmar quake
Rescue hopes fading three days after deadly Myanmar quake
-
'Basketbrawl' as seven ejected in Pistons-Wolves clash

-
 Four men loom large in Microsoft history
Four men loom large in Microsoft history
-
Computer pioneer Microsoft turns 50 in the age of AI

-
 Trump calls out both Putin and Zelensky over ceasefire talks
Trump calls out both Putin and Zelensky over ceasefire talks
-
Kim Hyo-joo tops Vu in playoff to win LPGA Ford Championship

-
 Economy and especially Trump: Canadians' thoughts on campaigns
Economy and especially Trump: Canadians' thoughts on campaigns
-
Liberal PM Carney takes lead four weeks before Canada vote

-
 SpaceX to launch private astronauts on first crewed polar orbit
SpaceX to launch private astronauts on first crewed polar orbit
-
Australia open door for Kerr's return as Matildas captain

-
 The Premier League's unlikely pretenders to Champions League riches
The Premier League's unlikely pretenders to Champions League riches
-
IFabric Corp Reports Record Q4 and Full Year 2024 Revenues and Strong Profitability


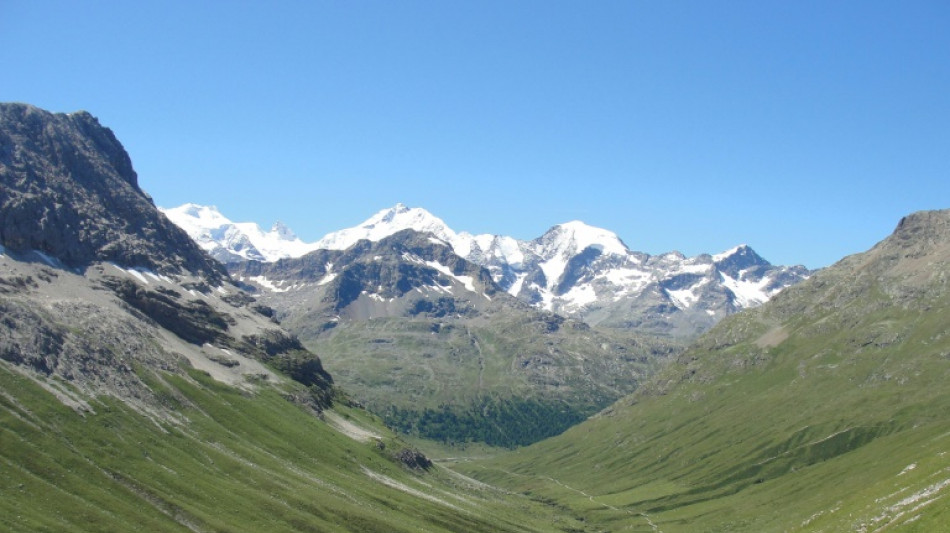
Seen from space, the snow-capped Alps are going green
The famous snow-capped peaks of the Alps are fading fast and being replaced by vegetation cover -- a process called "greening" that is expected to accelerate climate change, a study said Thursday.
The research, published in Science, was based on 38 years of satellite imagery across the entirety of the iconic European mountain range.
"We were very surprised, honestly, to find such a huge trend in greening," first author Sabine Rumpf, an ecologist at the University of Basel, told AFP.
Greening is a well-recognized phenomenon in the Arctic, but until now hadn't been well established over a large scale in mountainous areas.
However, since both the poles and mountains are warming faster than the rest of the planet, researchers suspected comparable effects.
For their analysis, the team examined regions at 1,700 meters above sea level, to exclude areas used for agriculture. They also excluded forested areas and glaciers.
According to the findings, which covered 1984-2021, snow cover was no longer present in summer on nearly 10 percent of the area studied.
Rumpf pointed out that satellite images can only verify the presence or absence of snow -- but the first effect of warming is to reduce the depth of the snowpack, which can't be seen from space.
Secondly, the researchers compared the amount of vegetation using wavelength analysis to detect the amount of chlorophyll present, and found plant growth increased across 77 percent of the zone studied.
- Vicious cycle -
Greening happens in three different ways: plants begin growing in areas they previously weren't present, they grow taller and more densely due to favorable conditions, and finally particular species growing normally at lower altitudes move into higher areas.
"It is climate change that is driving these changes," said Rumpf.
"Warming means that we have longer vegetation periods, we have more benign conditions that foster plant growth, so plants can just grow more and faster," she added.
The effect is additive: "The warmer it gets, the more precipitation falls as rain rather than snow."
And there are several harmful consequences.
First, a large part of drinking water comes from melting snow. If water is not stored as snow, it disappears faster via rivers.
Next, the habitat species adapted specifically to the alpine environment is disrupted.
The snow's disappearance also harms the tourism industry, a key economic driver for the region.
"What we kind of tend to forget is the emotional aspects of these processes that the Alps are like a very iconic symbol and when people think about Switzerland, it's usually the Alps that they think about," stressed Rumpf.
While alpine greening could increase carbon sequestration, feedback loops are more likely to cause a net result of amplified warming, and thawing of permafrost, the researchers argue.
Snow reflects about 90 percent of solar radiation, vegetation absorbs much more, and radiates the energy back in the form of heat -- which in turn further accelerates warming, snow melt, and more vegetation: a vicious cycle.
- From green to brown? -
The future of the Alps can't be predicted with certainty.
"In terms of snow, it's pretty straightforward," said Rumpf. "I would expect the snow cover to disappear more and more, especially at lower elevations."
For the time being, another phenomenon known as "browning" -- in which the ground is no longer covered with either snow or vegetation -- has only been detected in less than one percent of the area studied.
This is much less than what has been observed in the Arctic, or in the mountains of Central Asia.
It is fueled by two factors: the increase in episodes of extreme rain followed by droughts, and a reduction in water available to plants that was produced by annual snowmelt.
"We do not know for the future whether browning is going to occur more and more," concluded Rumpf, who hopes to repeat the observations in a few years' time.
F.Bennett--AMWN

