
-
 Less Soviet, more inspiring: Kyrgyzstan seeks new anthem
Less Soviet, more inspiring: Kyrgyzstan seeks new anthem
-
Defending champion Kyren Wilson crashes out in first round of World Snooker Championship

-
 NASA's oldest active astronaut returns to Earth on 70th birthday
NASA's oldest active astronaut returns to Earth on 70th birthday
-
Exec linked to Bangkok building collapse arrested

-
 Zelensky says Russian attacks ongoing despite Putin's Easter truce
Zelensky says Russian attacks ongoing despite Putin's Easter truce
-
Vaibhav Suryavanshi: the 14-year-old whose IPL dream came true

-
 Six drowning deaths as huge waves hit Australian coast
Six drowning deaths as huge waves hit Australian coast
-
Ukrainian soldiers' lovers kept waiting as war drags on

-
 T'Wolves dominate Lakers, Nuggets edge Clippers as NBA playoffs start
T'Wolves dominate Lakers, Nuggets edge Clippers as NBA playoffs start
-
Taxes on super rich and tech giants stall under Trump

-
 Star Wars series 'Andor' back for final season
Star Wars series 'Andor' back for final season
-
Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city

-
 Tariffs could lift Boeing and Airbus plane prices even higher
Tariffs could lift Boeing and Airbus plane prices even higher
-
Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China

-
 Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big MLS crowd in Cleveland
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big MLS crowd in Cleveland
-
Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan

-
 'Pandora's box': alarm bells in Indonesia over rising military role
'Pandora's box': alarm bells in Indonesia over rising military role
-
Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet

-
 Trio share lead at tight LA Championship
Trio share lead at tight LA Championship
-
Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town

-
 Recovering pope expected to delight crowds at Easter Sunday mass
Recovering pope expected to delight crowds at Easter Sunday mass
-
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win

-
 Force skipper clueless about extra-time rules in pulsating Super Rugby draw
Force skipper clueless about extra-time rules in pulsating Super Rugby draw
-
DEA MARIJUANA SCAM: As DEA Cannabis Program Implodes This 4/20, MMJ Stands Alone in Pursuit of Real Medicine

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big crowd in Cleveland

-
 Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
-
Another round of anti-Trump protests hits US cities

-
 'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
-
PSG maintain unbeaten Ligue 1 record, Marseille back up to second

-
 US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to block Trump deportations

-
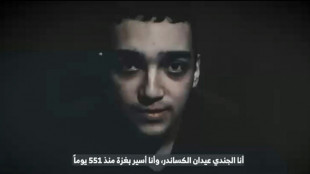 Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
-
Pacers thump Bucks to open NBA playoffs

-
 Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
-
Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations

-
 'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
-
DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
-
 England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
-
Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah

-
 McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
-
Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
-
Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League

-
 Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
-
Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling

-
 'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
-
Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit

-
 Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
-
PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season


What looming La Nina means for global temperatures
El Nino, the natural weather phenomenon that contributed to 2023 being the hottest year on record, has recently subsided, paving the way for its opposing, cooling La Nina phase to begin.
But in the context of a warming planet due to human-caused climate change, scientists say that cooling effect may be miniscule.
Here is how the cycle called El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) works to affect global weather:
- El Nino -
El Nino can weaken consistent trade winds that blow east to west across the tropical Pacific, influencing weather by affecting the movement of warm water across this vast ocean.
This weakening warms the usually cooler central and eastern sides of the ocean, altering rainfall over the equatorial Pacific and wind patterns that change temperature and rain around the world.
The extra heat at the surface of the Pacific releases energy into the atmosphere that can temporarily drive up global temperatures, which is why El Nino years are often among the warmest on record.
It occurs every two to seven years, and lasts nine to 12 months.
The latest El Nino, which began in June 2023, peaked among the five strongest such events on record, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
It typically results in drier conditions across southeast Asia, Australia, southern Africa, and northern South America, and conversely much wetter conditions in the Horn of Africa and the southern United States.
While it is unclear what impact climate change may be having on ENSO, it is affecting how these events play out, said Michelle L'Heureux, lead ENSO forecaster for the US NOAA weather agency.
Climate change is making extreme events more frequent and intense, and when colliding with ENSO can cause its associated drier or wetter conditions to "become more amplified", she added.
The elevated global temperatures ENSO causes also served as a "portal" into the future of climate change, L'Heureux said.
"It gives you... a bit of a preview of what a warmer world looks like because it is giving you a temporary boost. So we're now at a new level we haven't seen before," she said.
- Neutral period -
Although El Nino has been dissipating, the first four months of 2024 have continued to break heat records -- unsurprisingly as the cycle typically drives up temperatures the year after it develops.
ENSO is "not an on-off switch", L'Heureux explained. "It takes a while for the global atmospheric circulation to adjust."
Scientists anticipate that the neutral period between the two cycles will begin between May and July.
Above-normal temperatures are forecast to persist through July across the northern and southern hemispheres, with just equatorial regions anticipated to see near-to-below normal temperatures, according to WMO.
The neutral period is not likely to last long, L'Heureux explained.
Typically, after a strong El Nino as the world just experienced, La Nina soon follows.
- La Nina -
La Nina sees the eastern Pacific Ocean cool for a period of about one to three years, generating the opposite effects to El Nino on global weather.
It leads to wetter conditions in parts of Australia, southeast Asia, India, southeast Africa and northern Brazil, while causing drier conditions in parts of South America.
It can also contribute to more severe Atlantic hurricanes, and NOAA has forecast an "extraordinary" storm season ahead this year.
La Nina tends to bring down global temperatures, although L'Heureux warned against hopes of relief in areas like southeast Asia that have recently be battered by scorching heatwaves.
"The world is warming and ENSO is acting secondary to that," she said.
"Even this year with La Nina potentially developing, we're still expecting basically a top-five global mean temperature record," she said.
NOAA says there is a 69 percent chance of La Nina beginning sometime between July and September.
L.Miller--AMWN



