
-
 Putin evokes WWII victory to rally Russia behind Ukraine offensive
Putin evokes WWII victory to rally Russia behind Ukraine offensive
-
China exports beat forecasts ahead of US tariff talks

-
 Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
Leo XIV, the 'Latin Yankee', to celebrate first mass as pope
-
Most stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal

-
 IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
IPL suspended indefinitely over India-Pakistan conflict: reports
-
German lender Commerzbank's profits jump as it fends off UniCredit

-
 Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
Rare bone-eroding disease ruining lives in Kenya's poorest county
-
India says repulsed fresh Pakistan attacks as de-escalation efforts grow

-
 Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
Zhao's historic snooker title sparks talk of China world domination
-
'High expectations': EU looks to Merz for boost in tough times

-
 Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
Poisoned guests rarely invited before deadly mushroom lunch, Australia trial hears
-
China sales to US slump even as exports beat forecasts

-
 Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
Indian cricket to make 'final decision' on IPL over Pakistan conflict
-
Dethroned Bundesliga champions Leverkusen face uncertain future

-
 China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
China can play hardball at looming trade talks with US: analysts
-
French monuments in trouble while PSG prepare for Champions League final

-
 Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
Newcastle face Chelsea in top five showdown, Alexander-Arnold in spotlight
-
Flick's Barca must show 'hunger' in crunch Liga Clasico

-
 Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
Clasico the last chance saloon for Ancelotti's Real Madrid
-
Timberwolves overpower Warriors to level series

-
 Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
Chinese fabric exporters anxious for US trade patch-up
-
Putin gears up to host world leaders at lavish army parade

-
 Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
Nearing 100, Malaysian ex-PM Mahathir blasts 'old world' Trump
-
Leo XIV, first US pope, to celebrate first mass as pontiff

-
 Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
Asian stocks lifted by hopes for US-China talks after UK deal
-
Former head of crypto platform Celsius sentenced 12 years

-
 Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
Ex-model testifies in NY court that Weinstein assaulted her at 16
-
Genflow Biosciences PLC Announces Share Subscription, Director's Dealing and Update

-
 Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
Argo Blockchain PLC Announces 2024 Annual Results and Restoration of Listing
-
'Great honor': world leaders welcome first US pope

-
 Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
Pacquiao to un-retire and fight Barrios for welterweight title: report
-
Trump unveils UK trade deal, first since tariff blitz

-
 Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
Man Utd one step away from Europa League glory despite horror season
-
Jeeno shines on greens to grab LPGA lead at Liberty National

-
 Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
Mitchell fires PGA career-low 61 to grab Truist lead
-
AI tool uses selfies to predict biological age and cancer survival

-
 Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
Extremely online new pope unafraid to talk politics
-
Postecoglou hits back as Spurs reach Europa League final

-
 Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
Chelsea ease into Conference League final against Betis
-
Pope Leo XIV: Soft-spoken American spent decades amid poor in Peru

-
 First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
First US pope shared articles critical of Trump, Vance
-
'Inexcusable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip

-
 US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
US automakers blast Trump's UK trade deal
-
Stocks mostly rise as US-UK unveil trade deal

-
 Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
Trump presses Russia for unconditional 30-day Ukraine ceasefire
-
Anything but Europa League glory 'means nothing' for Man Utd: Amorim

-
 'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
'Inexcuseable' - NBA champs Boston in trouble after letting big leads slip
-
Pope Leo 'fell in love with Peru'and ceviche: Peru bishop

-
 Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
Pakistan's T20 cricket league moved to UAE over India conflict
-
India tells X to block over 8,000 accounts

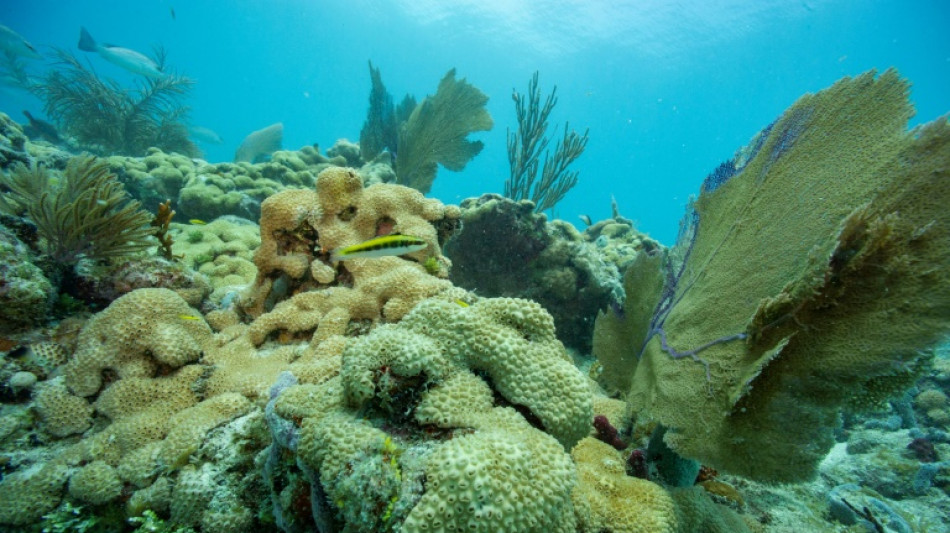
Burning question: what can we expect in a 1.5C world?
Massive wildfires exposing millions to toxic smoke, drought shrivelling crops and key waterways, destructive storms supercharged by record ocean temperatures -- in the last year the world has had a taste of what to expect with warming of 1.5C.
For the first time on record, Earth has endured 12 consecutive months of temperatures 1.5 degrees Celsius hotter than the pre-industrial era, Europe's climate monitor said Thursday.
That does not signal a breach of the more ambitious limit agreed by countries in the 2015 Paris Agreement -- because that is measured as an average over two decades.
Temperatures since the middle of last year have been ramped up by the naturally-occurring El Nino warming event, which is likely to recede in the coming months.
But underlying planetary heating has cranked up the global thermometer, driven largely by the burning of fossil fuels as well as deforestation and agriculture.
"Although this news does not mean the Paris limit is exceeded, it is undeniably bad news," said Joeri Rogelj, director of research at the Grantham Institute, Imperial College London.
"Unless global emissions are urgently brought down to zero, the world will soon fly past the safety limits set out in the Paris climate agreement."
- Limits of endurance -
That 1.5C milestone is no longer in the distant future, with the UN's IPCC climate science panel warning that a breach is likely sometime between 2030 and 2035.
What would a 1.5C world mean for humans and the natural world they rely on to survive?
Scientists estimate current global temperatures are around 1.2C hotter overall than the pre-industrial benchmark, averaged across the period 1850 to 1900.
Severe climate impacts are already visible around the world and would be amplified once the 1.5C threshold is reached.
Some parts of the world, like the Arctic and high mountain areas, are warming far faster than others.
In other regions, even small temperature increases can expose vulnerable communities to dangerous threats, including heat that tests the very limit of human endurance.
Coral reefs -- ecosystems that provide habitat for an immense array of marine life and protect coastlines -- are projected to decline 70 to 90 percent in a world that has warmed 1.5C.
The loss of biodiversity globally will be among the most pronounced impacts of a 1.5C warmer climate, according to the IPCC.
- Over the line -
Climate experts are also concerned that accelerating permafrost thaw will release carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, creating a vicious cycle of warming.
The IPCC currently classifies the risk of permafrost melt in some regions as "moderate", but it would become "high" in a 1.5C or even warmer climate.
Some impacts of warming are already irreversible, and will continue to worsen, like sea level rise, driven by melting ice sheets and glaciers.
Higher ocean levels are already threatening the future of low-lying islands, while in the longer term metres of sea level rise will likely swamp many of the world's major coastal cities.
Even if the 1.5C limit is breached, reducing greenhouse gas emissions remains crucial to stay "well below" 2C of warming, the maximum warming limit set by the Paris Agreement.
That is because "every increment of global warming will intensify multiple and concurrent hazards," the IPCC warns.
Halting deforestation and the rampant destruction of ecosystems are also crucial to maintain nature's ability to drawn down carbon from the atmosphere.
Oceans absorb 90 percent of the excess heat produced by the carbon pollution from human activity since the dawn of the industrial age.
A.Jones--AMWN



