
-
 Saka 'ready to go' after long injury lay-off: Arteta
Saka 'ready to go' after long injury lay-off: Arteta
-
Ingebrigtsen Sr, on trial for abusing Olympic champion, says he was 'overly protective'

-
 Tourists and locals enjoy 'ephemeral' Tokyo cherry blossoms
Tourists and locals enjoy 'ephemeral' Tokyo cherry blossoms
-
Khamenei warns of 'strong' response if Iran attacked

-
 France fines Apple 150 million euros over privacy feature
France fines Apple 150 million euros over privacy feature
-
UK PM urges nations to smash migrant smuggling gangs 'once and for all'

-
 Thai authorities probe collapse at quake-hit construction site
Thai authorities probe collapse at quake-hit construction site
-
France's Le Pen convicted in fake jobs trial

-
 Chinese tech giant Huawei says profits fell 28% last year
Chinese tech giant Huawei says profits fell 28% last year
-
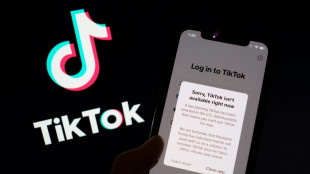
Trump says confident of TikTok deal before deadline
-
 Myanmar declares week of mourning as hopes fade for quake survivors
Myanmar declares week of mourning as hopes fade for quake survivors
-
Japan's Nikkei leads hefty market losses, gold hits record

-
 Tears in Taiwan for relatives hit by Myanmar quake
Tears in Taiwan for relatives hit by Myanmar quake
-
Venezuela says US revoked transnational oil, gas company licenses

-
 'Devastated': Relatives await news from Bangkok building collapse
'Devastated': Relatives await news from Bangkok building collapse
-
Arsenal, Tottenham to play pre-season North London derby in Hong Kong

-
 Japan's Nikkei leads hefty equity market losses; gold hits record
Japan's Nikkei leads hefty equity market losses; gold hits record
-
Israel's Netanyahu picks new security chief, defying legal challenge

-
 Trump says US tariffs to hit 'all countries'
Trump says US tariffs to hit 'all countries'
-
Prayers and tears for Eid in quake-hit Mandalay

-
 After flops, movie industry targets fresh start at CinemaCon
After flops, movie industry targets fresh start at CinemaCon
-
Tsunoda targets podium finish in Japan after 'unreal' Red Bull move

-
 French chefs await new Michelin guide
French chefs await new Michelin guide
-
UK imposes travel permit on Europeans from Wednesday

-
 At his academy, Romanian legend Hagi shapes future champions
At his academy, Romanian legend Hagi shapes future champions
-
Referee's lunch break saved Miami winner Mensik from early exit

-
 Djokovic refuses to discuss eye ailment after shock Miami loss
Djokovic refuses to discuss eye ailment after shock Miami loss
-
Mitchell magic as Cavs bag 60th win, Pistons and T'Wolves brawl

-
 Mensik shocks Djokovic to win Miami Open
Mensik shocks Djokovic to win Miami Open
-
Duterte lawyer: 'compelling' grounds to throw case out

-
 What happens on Trump's 'Liberation Day' and beyond?
What happens on Trump's 'Liberation Day' and beyond?
-
Clock ticks on Trump's reciprocal tariffs as countries seek reprieve

-
 Japan-Australia flagship hydrogen project stumbles
Japan-Australia flagship hydrogen project stumbles
-
Musk deploys wealth in bid to swing Wisconsin court vote

-
 Mensik upsets Djokovic to win Miami Open
Mensik upsets Djokovic to win Miami Open
-
China manufacturing activity grows at highest rate in a year

-
 'Waited for death': Ex-detainees recount horrors of Sudan's RSF prisons
'Waited for death': Ex-detainees recount horrors of Sudan's RSF prisons
-
Japan's Nikkei leads big losses in Asian markets as gold hits record

-
 Rescue hopes fading three days after deadly Myanmar quake
Rescue hopes fading three days after deadly Myanmar quake
-
'Basketbrawl' as seven ejected in Pistons-Wolves clash

-
 Four men loom large in Microsoft history
Four men loom large in Microsoft history
-
Computer pioneer Microsoft turns 50 in the age of AI

-
 Trump calls out both Putin and Zelensky over ceasefire talks
Trump calls out both Putin and Zelensky over ceasefire talks
-
Kim Hyo-joo tops Vu in playoff to win LPGA Ford Championship

-
 Economy and especially Trump: Canadians' thoughts on campaigns
Economy and especially Trump: Canadians' thoughts on campaigns
-
Liberal PM Carney takes lead four weeks before Canada vote

-
 SpaceX to launch private astronauts on first crewed polar orbit
SpaceX to launch private astronauts on first crewed polar orbit
-
Australia open door for Kerr's return as Matildas captain

-
 The Premier League's unlikely pretenders to Champions League riches
The Premier League's unlikely pretenders to Champions League riches
-
IFabric Corp Reports Record Q4 and Full Year 2024 Revenues and Strong Profitability


UN report to lay out options to halt climate crisis
Nearly 200 nations gather on Monday to confront a question that will outlive Russia's invasion of Ukraine: how do we stop carbon pollution overheating the planet and threatening life as we know it?
The answer is set to arrive on April 4 after closed-door, virtual negotiations approve the summary of a phonebook-sized report detailing options for drawing down greenhouse gases and extracting them out of thin air.
"The science is crystal clear, the impacts are costly and mounting, but we still have some time to close the window and get ahead of the worst of them if we act now," said Alden Meyer, a senior analyst at climate and energy think tank E3G.
"This report will supply the answers as to what we need if we're serious about getting there."
In August 2021, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) laid out the physical science: changes in global warming and sea level rise, along with shifts in the frequency, duration and intensity of cyclones, heatwaves, droughts and other forms of extreme weather.
That was the first instalment of a three-part assessment, the sixth since 1990. It projected that Earth's surface temperature will rise 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, perhaps within a decade.
A 1.5C cap on global warming -- the aspirational goal of the 2015 Paris climate accord -- has been embraced as a target by most of the world's nations.
Current carbon-cutting commitments under the treaty, however, still put us on a catastrophic path toward 2.7C of warming by 2100.
- A liveable future -
Part two of the more than 10,000-page report -- described by UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres as an "atlas of human suffering" -- catalogued past and future climate impacts on human society and the natural world.
Delaying climate action would severely reduce the chances of a "livable future," it concluded.
Part three -- spread across thousands of pages -- is about how to slow and stop warming, with separate chapters on the key sectors where rapid and deep change is critical: energy, transport, industry, agriculture, among others.
"We are talking about the large-scale transformation of all the major systems," climate economist and co-author Celine Guivarch told AFP.
It also focuses on ways to curb carbon emissions by reducing demand, whether through making buildings more energy efficient or encouraging shifts in lifestyle, such as eating less beef and not flying half-way around the world for a week-long holiday.
The report details more than a dozen techniques for pulling CO2 out of the air, which will be needed to compensate for sectors -- such as aviation and shipping -- that are likely still carbon polluters by mid-century.
"Many things have changed" since the previous three-part report, which came out eight years ago, said Taryn Fransen, an analyst at the World Resources Institute.
The Paris Agreement -- the first climate deal in which all countries pledged action -- was signed.
The world has seen an endless crescendo of deadly climate impacts, from drought to fire to floods.
The price of renewable energy, key to the reducing emissions, has fallen below the cost of fossil fuels in most markets.
- 'Inflamed situation' -
The IPCC "solutions" report draws from hundreds of models projecting development pathways that keep Earth within the bounds of the Paris temperature goals.
"There are scenarios that show high renewables and low nuclear, and scenarios that show the opposite," said Fransen.
"This report lays out those pathways. Now it's up now to our leaders to take that to heart."
Besides feeding into UN political negotiations, which resume in November in Egypt at COP 27, the IPCC findings will also be important "for the conversation going on in the US and Europe around the need to transition away from Russian oil and gas," said Meyer.
The head of the IPCC delegation from Ukraine made this point in a dramatic statement at a closed plenary in February, only days after Russian troops invaded her country.
"Human-induced climate change and the war on Ukraine have the same roots -- fossil fuels -- and our dependence on them," said Svitlana Krakovska, according to multiple sources.
The war in Ukraine will likely come up during the two-week IPCC negotiations starting Monday.
"It's a more enflamed situation," said Meyer. "I don't know how this is gonna play out but it's something to watch."
P.Stevenson--AMWN

