-
 Asian markets edge up but uncertainty rules ahead of Trump tariffs
Asian markets edge up but uncertainty rules ahead of Trump tariffs
-
Nintendo's megahit Switch console: what to know

-
 Nintendo to unveil upgrade to best-selling Switch console
Nintendo to unveil upgrade to best-selling Switch console
-
China practises hitting key ports, energy sites in Taiwan drills

-
 Oil, sand and speed: Saudi gearheads take on towering dunes
Oil, sand and speed: Saudi gearheads take on towering dunes
-
All eyes on Tsunoda at Japan GP after ruthless Red Bull move

-
 'Image whisperers' bring vision to the blind at Red Cross museum
'Image whisperers' bring vision to the blind at Red Cross museum
-
Hay shines as New Zealand make 292-8 in Pakistan ODI

-
 Other governments 'weaponising' Trump language to attack NGOs: rights groups
Other governments 'weaponising' Trump language to attack NGOs: rights groups
-
UK imposes online entry permit on European visitors

-
 How a Brazilian chief is staving off Amazon destruction
How a Brazilian chief is staving off Amazon destruction
-
Meme politics: White House embraces aggressive alt-right online culture

-
 China launches military drills in Taiwan Strait
China launches military drills in Taiwan Strait
-
US senator smashes record with 25-hour anti-Trump speech

-
 Brazil binman finds newborn baby on garbage route
Brazil binman finds newborn baby on garbage route
-
US senator smashes record with marathon anti-Trump speech

-
 Trump advisor Waltz faces new pressure over Gmail usage
Trump advisor Waltz faces new pressure over Gmail usage
-
Niger junta frees ministers of overthrown government

-
 Trump set to unleash 'Liberation Day' tariffs
Trump set to unleash 'Liberation Day' tariffs
-
Boeing chief to acknowledge 'serious missteps' at US Senate hearing

-
 Real Madrid hold Real Sociedad in eight-goal thriller to reach Copa del Rey final
Real Madrid hold Real Sociedad in eight-goal thriller to reach Copa del Rey final
-
Nuno salutes 'special' Elanga after stunning strike fires Forest

-
 PSG survive scare against Dunkerque to reach French Cup final
PSG survive scare against Dunkerque to reach French Cup final
-
Sundowns edge Esperance as crowd violence mars quarter-final

-
 Nottingham Forest beat Man Utd, Saka scores on Arsenal return
Nottingham Forest beat Man Utd, Saka scores on Arsenal return
-
Elanga wonder-goal sinks Man Utd as Forest eye Champions League berth

-
 Stock markets mostly advance ahead of Trump tariffs deadline
Stock markets mostly advance ahead of Trump tariffs deadline
-
US movie theaters urge 45-day 'baseline' before films hit streaming

-
 Saka scores on return as Arsenal beat Fulham
Saka scores on return as Arsenal beat Fulham
-
Third-division Bielefeld shock holders Leverkusen in German Cup

-
 Ball-blasting 'Torpedo bats' making waves across MLB opening weekend
Ball-blasting 'Torpedo bats' making waves across MLB opening weekend
-
Newsmax shares surge more than 2,000% in days after IPO

-
 Thousands of Hungarians protest against Pride ban law
Thousands of Hungarians protest against Pride ban law
-
GM leads first quarter US auto sales as tariffs loom

-
 Tesla sales tumble in Europe in the first quarter
Tesla sales tumble in Europe in the first quarter
-
No 'eye for an eye' approach to US tariffs: Mexico

-
 NFL club owners back dynamic kickoffs, delay tush push vote
NFL club owners back dynamic kickoffs, delay tush push vote
-
Trump 'perfecting' new tariffs as nervous world braces

-
 Trump nominee says to press UK on Israel arms
Trump nominee says to press UK on Israel arms
-
French court says Le Pen appeal ruling could come before presidential vote

-
 The battle to control assets behind Bosnia crisis
The battle to control assets behind Bosnia crisis
-
Prabhsimran powers Punjab to IPL win over Lucknow

-
 Mass layoffs targeting 10,000 jobs hit US health agencies
Mass layoffs targeting 10,000 jobs hit US health agencies
-
Tiger's April Foolishness: plan to play Masters just a joke

-
 Myanmar quake toll passes 2,700, nation halts to honour victims
Myanmar quake toll passes 2,700, nation halts to honour victims
-
Turkish fans, artists urge Muse to cancel Istanbul gig

-
 US seeks death penalty for accused killer of insurance CEO
US seeks death penalty for accused killer of insurance CEO
-
UK govt moves to block sentencing guidelines for minority defendants

-
 Trump puts world on edge as 'Liberation Day' tariffs loom
Trump puts world on edge as 'Liberation Day' tariffs loom
-
Swedish journalist jailed in Turkey kept 'isolated': employer


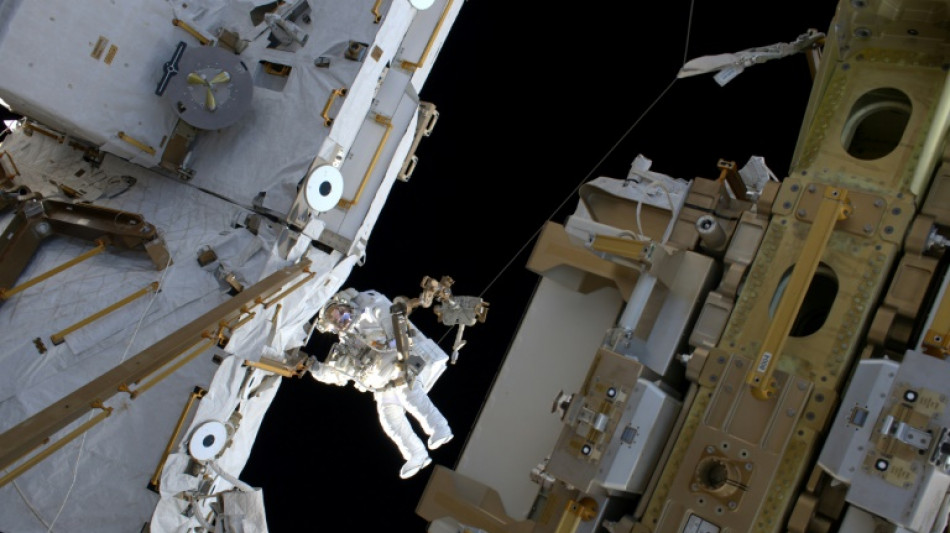
Lost in space: Astronauts struggle to regain bone density
Astronauts lose decades' worth of bone mass in space that many do not recover even after a year back on Earth, researchers said Thursday, warning that it could be a "big concern" for future missions to Mars.
Previous research has shown astronauts lose between one to two percent of bone density for every month spent in space, as the lack of gravity takes the pressure off their legs when it comes to standing and walking.
To find out how astronauts recover once their feet are back on the ground, a new study scanned the wrists and ankles of 17 astronauts before, during and after a stay on the International Space Station.
The bone density lost by astronauts was equivalent to how much they would shed in several decades if they were back on Earth, said study co-author Steven Boyd of Canada's University of Calgary and director of the McCaig Institute for Bone and Joint Health.
The researchers found that the shinbone density of nine of the astronauts had not fully recovered after a year on Earth -- and were still lacking around a decade's worth of bone mass.
The astronauts who went on the longest missions, which ranged from four to seven months on the ISS, were the slowest to recover.
"The longer you spend in space, the more bone you lose," Boyd told AFP.
Boyd said it is a "big concern" for planned for future missions to Mars, which could see astronauts spend years in space.
"Will it continue to get worse over time or not? We don't know," he said.
"It's possible we hit a steady state after a while, or it's possible that we continue to lose bone. But I can't imagine that we'd continue to lose it until there's nothing left."
A 2020 modelling study predicted that over a three-year spaceflight to Mars, 33 percent of astronauts would be at risk of osteoporosis.
Boyd said some answers could come from research currently being carried out on astronauts who spent at least a year onboard the ISS.
Guillemette Gauquelin-Koch, the head of medicine research at France's CNES space agency, said that the weightlessness experienced in space is "most drastic physical inactivity there is".
"Even with two hours of sport a day, it is like you are bedridden for the other 22 hours," said the doctor, who was not part of the study.
"It will not be easy for the crew to set foot on Martian soil when they arrive -- it's very disabling."
- 'The silent disease' -
The new study, which was published in Scientific Reports, also showed how spaceflight alters the structure of bones themselves.
Boyd said that if you thought of a body's bones like the Eiffel Tower, it would as if some of the connecting metal rods that hold the structure up were lost.
"And when we return to Earth, we thicken up what's remaining, but we don't actually create new rods," he said.
Some exercises are better for retaining bone mass than others, the study found.
Deadlifting proved significantly more effective than running or cycling, it said, suggesting more heavy lower-body exercises in the future.
But the astronauts -- who are mostly fit and in their 40s -- did not tend to notice the drastic bone loss, Boyd said, pointing out that the Earth-bound equivalent osteoporosis is known as "the silent disease".
Canadian astronaut Robert Thirsk, who has spent the most time in space, said that for him bones and muscles took the longest to recover after spaceflight.
"But within a day of landing, I felt comfortable again as an Earthling," he said in a statement accompanying the research.
P.Silva--AMWN