-
 No.1 Scheffler goes for third Masters crown in four years
No.1 Scheffler goes for third Masters crown in four years
-
Where Trump's tariffs could hurt Americans' wallets

-
 Trump says 'very close to a deal' on TikTok
Trump says 'very close to a deal' on TikTok
-
Trump tariffs on Mexico: the good, the bad, the unknown

-
 Postecoglou denies taunting Spurs fans in Chelsea defeat
Postecoglou denies taunting Spurs fans in Chelsea defeat
-
Oscar-winning Palestinian director speaks at UN on Israeli settlements

-
 With tariff war, Trump also reshapes how US treats allies
With tariff war, Trump also reshapes how US treats allies
-
Fernandez fires Chelsea into fourth as pressure mounts on Postecoglou

-
 South Korea court to decide impeached president's fate
South Korea court to decide impeached president's fate
-
Penguin memes take flight after Trump tariffs remote island

-
 E.T., no home: Original model of movie alien doesn't sell at auction
E.T., no home: Original model of movie alien doesn't sell at auction
-
Italy's Brignone has surgery on broken leg with Winter Olympics looming

-
 Trump defiant as tariffs send world markets into panic
Trump defiant as tariffs send world markets into panic
-
City officials vote to repair roof on home of MLB Rays

-
 Rockets forward Brooks gets one-game NBA ban for technicals
Rockets forward Brooks gets one-game NBA ban for technicals
-
Pentagon watchdog to probe defense chief over Signal chat row

-
 US tariffs could push up inflation, slow growth: Fed official
US tariffs could push up inflation, slow growth: Fed official
-
New Bruce Springsteen music set for June 27 release

-
 Tom Cruise pays tribute to Val Kilmer
Tom Cruise pays tribute to Val Kilmer
-
Mexico president welcomes being left off Trump's tariffs list

-
 Zuckerberg repeats Trump visits in bid to settle antitrust case
Zuckerberg repeats Trump visits in bid to settle antitrust case
-
US fencer disqualified for not facing transgender rival

-
 'Everyone worried' by Trump tariffs in France's champagne region
'Everyone worried' by Trump tariffs in France's champagne region
-
Italy's Brignone suffers broken leg with Winter Olympics looming

-
 Iyer blitz powers Kolkata to big IPL win over Hyderabad
Iyer blitz powers Kolkata to big IPL win over Hyderabad
-
Russian soprano Netrebko to return to London's Royal Opera House

-
 French creche worker gets 25 years for killing baby with drain cleaner
French creche worker gets 25 years for killing baby with drain cleaner
-
UK avoids worst US tariffs post-Brexit, but no celebrations

-
 Canada imposing 25% tariff on some US auto imports
Canada imposing 25% tariff on some US auto imports
-
Ruud wants 'fair share' of Grand Slam revenue for players

-
 Lesotho, Africa's 'kingdom in the sky' jolted by Trump
Lesotho, Africa's 'kingdom in the sky' jolted by Trump
-
Trump's trade math baffles economists

-
 Gaza heritage and destruction on display in Paris
Gaza heritage and destruction on display in Paris
-
'Unprecedented crisis' in Africa healthcare: report

-
 Pogacar gunning for blood and thunder in Tour of Flanders
Pogacar gunning for blood and thunder in Tour of Flanders
-
Macron calls for suspension of investment in US until tariffs clarified

-
 Wall St leads rout as world reels from Trump tariffs
Wall St leads rout as world reels from Trump tariffs
-
Mullins gets perfect National boost with remarkable four-timer

-
 Trump tariffs hammer global stocks, dollar and oil
Trump tariffs hammer global stocks, dollar and oil
-
Authors hold London protest against Meta for 'stealing' work to train AI

-
 Tate Modern gifted 'extraordinary' work by US artist Joan Mitchell
Tate Modern gifted 'extraordinary' work by US artist Joan Mitchell
-
Mexico president welcomes being left off Trump's new tariffs list

-
 Tonali eager to lead Newcastle back into Champions League
Tonali eager to lead Newcastle back into Champions League
-
Lesotho hardest hit as new US tariffs rattle Africa

-
 Stellantis pausing some Canada, Mexico production over Trump auto tariffs
Stellantis pausing some Canada, Mexico production over Trump auto tariffs
-
Rising odds asteroid that briefly threatened Earth will hit Moon
-
 Italy reels from Brignone broken leg with Winter Olympics looming
Italy reels from Brignone broken leg with Winter Olympics looming
-
Is the Switch 2 worth the price? Reviews are mixed

-
 Ancelotti’s tax trial wraps up in Spain with prosecutors seeking jail
Ancelotti’s tax trial wraps up in Spain with prosecutors seeking jail
-
Civilians act to bring aid to Myanmar earthquake victims


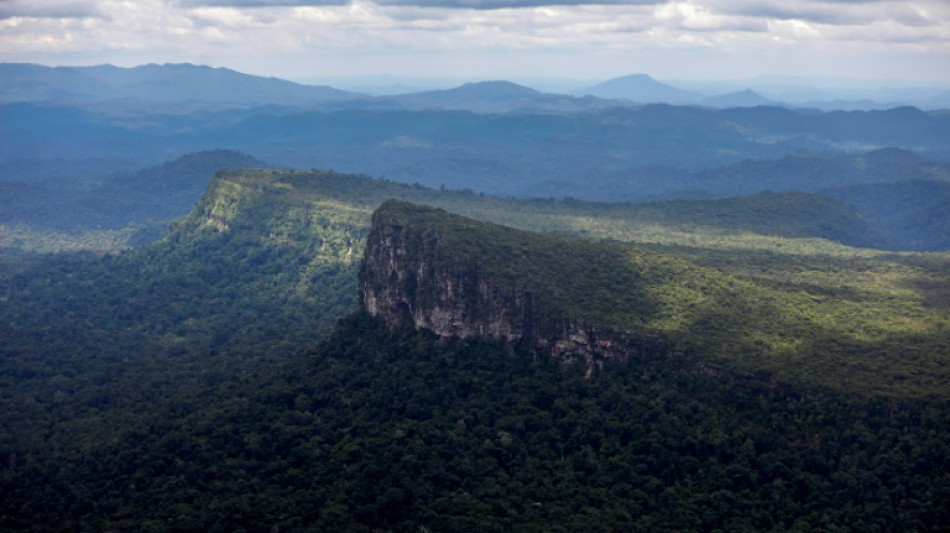
Amazon Indigenous lands prevent disease, save billions: study
Protected Indigenous reservations in the Amazon rainforest absorb thousands of tonnes of airborne pollution each year, saving around $2 billion annually in healthcare costs for treating respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, according to a study published Thursday.
The decade-long study analyzed the health impacts of forest fires in the Brazilian Amazon, which release huge amounts of particles into the atmosphere that can travel hundreds of kilometers (miles), damaging the air quality in distant cities.
By protecting their own lands against such fires -- often set by land-grabbers, cattle ranchers and others encroaching on the forest -- and instead saving pollution-absorbing trees, Amazon Indigenous peoples help prevent thousands of cases of potentially deadly diseases, found the study, published in the journal Communications, Earth & Environment.
"Worldwide, forests are known for absorbing pollutants from fires through pores on the surface of the leaves, but this is the first time we have estimated the capacity of tropical forests to do this," said lead author Paula Prist of US-based research group EcoHealth Alliance.
"Our results indicate that the Amazon rainforest can absorb as much as 26,000 metric tonnes of the particles every year, and Indigenous territories are responsible for 27 percent of this absorption," she said in a statement.
The study found Indigenous forests prevent 15 million cases of disease each year, saving the health care system at least $2 billion -- a conservative estimate, researchers said.
Numerous studies have found protected Indigenous lands play a key role in protecting forests, whose pollution-absorbing capacity makes them vital to the race to curb climate change.
Indigenous leaders said the new study adds yet another argument to the case for protecting native lands.
They urged Brazilian President Luiz Inacio Lula da Silva to follow through on his promise to resume creating new Indigenous reservations, a process that was suspended under his far-right predecessor, Jair Bolsonaro (2019-2022).
"This study reinforces what Indigenous peoples have been saying for ages," said Dinamam Tuxa, executive coordinator of the Association of Brazil's Indigenous Peoples (APIB).
"It demonstrates the importance of our territories in fighting dangerous pollution... and climate change."
Ch.Kahalev--AMWN