
-
 Sweden drowns in discarded fast fashion items
Sweden drowns in discarded fast fashion items
-
Rybakina powers Kazakhstan into Billie Jean King Cup finals

-
 Despite US tariffs pause, southern African economies under threat
Despite US tariffs pause, southern African economies under threat
-
A night at the Geneva opera -- that is a literal snoozefest

-
 Cash-strapped Nigerians turn to YouTube for entertainment
Cash-strapped Nigerians turn to YouTube for entertainment
-
Two dead as fans, police clash before Copa Libertadores game in Chile

-
 Flowers in their hair: Shan boys ordained into Buddhist monkhood
Flowers in their hair: Shan boys ordained into Buddhist monkhood
-
Edwards leads Wolves past Grizzlies as playoff race heats up

-
 Ancelotti questioned as Real Madrid face Alaves
Ancelotti questioned as Real Madrid face Alaves
-
Old foes Bayern and Dortmund face off amid spectre of European exit

-
 Early holiday, more fans: Philippines schools adapt to climate change
Early holiday, more fans: Philippines schools adapt to climate change
-
In skies, as on land, European forces face gaps if US pulls back

-
 Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?
Digital divas: Can Japan's virtual YouTuber craze crack America?
-
WHO pandemic agreement talks face deadline crunch
-
 Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns
Stocks, dollar sink and gold hits record as Trump tariff panic returns
-
LeMond hails 'one in a million' Pogacar ahead of Paris-Roubaix debut

-
 Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts
Liverpool can move closer to the title as top five tension mounts
-
Trump admits trade war 'cost' as markets hit

-
 AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game
AI only just beginning to revolutionize the NBA game
-
Despite Trump pause, overall US tariff rate at highest in a century

-
 'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims
'A pain that doesn't subside' at funerals for Dominican nightclub disaster victims
-
Panama deal allows US to deploy troops to canal

-
 US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves
US firm says it brought back extinct dire wolves
-
Grieving Dominicans start burying 220 victims of nightclub disaster

-
 Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National
Aberg closes strong at 'sneaky hard' Augusta National
-
US auto union praises some Trump tariffs

-
 Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
Australian IVF clinic admits embryo mix-up
-
Rose: I've played well enough to win Masters but lack the jacket

-
 Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead
Rose again enjoys 'luxury' of first-round Masters lead
-
Rose rockets to Masters lead, defending champ Scheffler in pursuit

-
 Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi
Tesla opens first showroom in oil-rich Saudi
-
Oscars to add new award for stunts

-
 Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'
Hatton loves being at Masters but 'It's just so hard'
-
'Mistakes can happen': Amorim backs Onana after Lyon nightmare

-
 RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'
RFK Jr says study will reveal cause of autism 'epidemic'
-
Tourist family, pilot killed in 'tragic' NY helicopter crash

-
 No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title
No.1 Scheffler makes strong Masters start to defend title
-
Man Utd and Spurs draw in Europa League, Rangers hold Athletic

-
 Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit
Rose rockets to Masters lead with Scheffler and McIlroy in pursuit
-
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors in Europa League

-
 Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors
Man Utd held late in Lyon after Onana errors
-
Wall Street rally fizzles as tariff fears resurface

-
 MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study
MLS to open 'second phase' of major season overhaul study
-
Argentina braves 24-hour strike as it awaits word on IMF loan

-
 Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard
Spain's Ballester finds relief in Masters water hazard
-
Porro rescues Postecoglou as Spurs held by Frankfurt

-
 Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster
Grieving Dominicans start burying 200+ victims of nightclub disaster
-
CONMEBOL proposes one-off 64-team World Cup in 2030

-
 Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup
Rybakina on form for Kazakhstan in BJK Cup
-
Former Real Madrid coach Leo Beenhakker dies aged 82


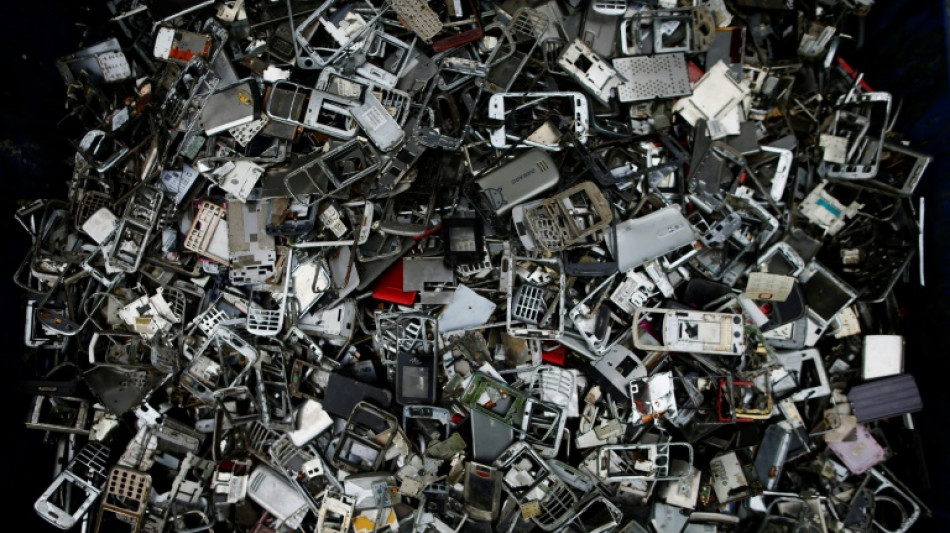
'Throwaway economy' thwarting climate goals: report
Countries are neglecting the massive impact of the "throwaway" economy on planet-warming emissions, according to research published Wednesday that calculated more than half a trillion tonnes of virgin materials have been consumed since the 2015 Paris climate deal.
From clothing to food, planes to buildings, research by the organisation Circle Economy estimates that 70 percent of greenhouse gas emissions are linked to the manufacturing and use of products.
But in its annual report on the state of the world's use of materials, researchers said national climate pledges to reduce emissions focus narrowly on fossil fuel use and ignore the mounting global appetite for stuff.
Matthew Fraser, head of research at Circle Economy, said the report aimed to look beyond just fossil fuel use and the transition to green energy and ask about the emissions implications of using fewer resources.
"What if we reimagine our relationship with stuff, what would that bring us? Actually, it is quite significant," he told AFP.
The report estimates that if the economy were more circular, reducing resource extraction and consumption by 28 percent, then the world could meet the Paris warming target of 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
But only a third of nations' climate pledges mention the circular economy as part of their emissions goals, the report said.
It warns that humanity is consuming 70 percent more virgin materials than the world can safely replenish.
- Economic 'metabolism' -
The analysis looks at global material flows based on national import and export figures and translates them into estimates of materials used -- and reused.
It calculates annual resource use has grown from 89.8 billion tonnes in 2016 to more than 100 billion tonnes in 2019 and estimated it at 101.4 billion last year.
Circle Economy found that almost all of the materials extracted go to waste, with just 8.6 percent of materials recycled in 2020, what they call the circularity gap.
That is an even lower proportion than in 2018, when reused materials were 9.1 percent of the total, as the global demand for more things surges.
"Even though we are getting more efficient with how we use materials -- computers are getting smaller, cars are becoming lighter, recycling is getting better -- these micro gains in efficiency just aren't stacking up relative to the total increasing demand," said Fraser.
The report identified a number of practices across sectors from food production to transportation that it said could help rein in the ever-expanding use of virgin materials.
Fraser said the model that enables people in richer countries to buy products from all over the world to be delivered within hours and days "will inevitably have to change".
The report also weighed strategies like enabling electrical goods -- which contain critical raw materials including gold, silver and cobalt -- to be repaired, redesigning items to be easier to recycle, restricting single-use plastics and renting items like cars rather than buying them.
One sector it identified as having a significant opportunity to reduce its materials footprint was buildings and construction, where Fraser said current practices were far from sustainable.
He said government policy would be needed occasionally to reconfigure the economic incentives that make reusing resources more expensive than using new ones -- stressing that this should be seen as an integral part of efforts to curb global warming.
But Fraser said for now the issue remains a significant blind spot for governments, which he said do not pull together data of their countries' materials footprint.
He added that people in the future may ask tougher questions about whether materials can be recycled before they are even used.
"Could we become more strict about the metabolism of our economy? Just like you wouldn't eat junk food all the time," he said.
"I think in the future that could become more and more prominent."
Y.Aukaiv--AMWN