
-
 Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
Neighbours improvise first aid for wounded in besieged Sudan city
-
Tariffs could lift Boeing and Airbus plane prices even higher

-
 Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
Analysts warn US could be handing chip market to China
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big MLS crowd in Cleveland

-
 Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
Social media helps fuel growing 'sex tourism' in Japan
-
'Pandora's box': alarm bells in Indonesia over rising military role

-
 Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
Alaalatoa hails 'hustling hard' Brumbies for rare Super Rugby clean sheet
-
Trio share lead at tight LA Championship

-
 Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
Sampdoria fighting relegation disaster as old heroes ride into town
-
Recovering pope expected to delight crowds at Easter Sunday mass

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Knicks and Pacers win
-
Force skipper clueless about extra-time rules in pulsating Super Rugby draw

-
 Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
Nuggets edge Clippers in NBA playoff overtime thriller, Pacers thump Bucks
-
Unbeaten Miami edge Columbus in front of big crowd in Cleveland

-
 Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
Kim takes one-shot lead over Thomas, Novak at RBC Heritage
-
Another round of anti-Trump protests hits US cities

-
 'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
'So grateful' - Dodgers star Ohtani and wife welcome first child
-
PSG maintain unbeaten Ligue 1 record, Marseille back up to second

-
 US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
US, Iran report progress in nuclear talks, will meet again
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to block Trump deportations

-
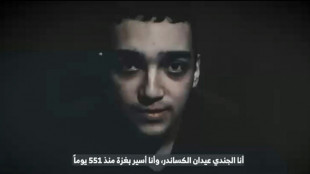 Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
Hamas armed wing says fate of US-Israeli captive unknown
-
Pacers thump Bucks to open NBA playoffs

-
 Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
Sabalenka reaches Stuttgart semis as Ostapenko extends Swiatek mastery
-
Zelensky says Ukraine will observe Putin's Easter truce but claims violations

-
 'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
'Fuming' Watkins fires Villa in bid to prove Emery wrong
-
DR Congo boat fire toll revised down to 33
-
 England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
England thrash Scotland to set up France Grand Slam showdown
-
Verstappen's Red Bull 'comes alive' to claim record pole in Jeddah

-
 McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
McTominay fires Napoli level with Inter as Conte fuels exit rumours
-
Rajasthan unleash Suryavanshi, 14, as youngest IPL player but lose thriller

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
Man City boost top five bid, Aston Villa thrash in-form Newcastle
-
Villa rout Newcastle to rekindle bid to reach Champions League

-
 Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
Dumornay gives Lyon lead over Arsenal in Women's Champions League semis
-
Trans rights supporters rally in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling

-
 'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
'We have to wait': Barca's Flick on Lewandowski injury fear
-
Bordeaux-Begles backups edge Pau to close in on Top 14 summit

-
 Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
Trans rights supporters rally outside in London, Edinburgh after landmark ruling
-
PSG beat Le Havre to stay on course for unbeaten Ligue 1 season

-
 Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League with Everton late show
-
14-year-old Vaibhav Suryavanshi becomes youngest IPL player

-
 Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
Barca make stunning comeback to beat Celta Vigo in Liga thriller
-
Zverev sets up birthday bash with Shelton in Munich

-
 Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller
Man City boost top five bid, Southampton snatch late leveller
-
US Supreme Court intervenes to pause Trump deportations

-
 Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final
Alcaraz and Rune race into Barcelona final
-
US, Iran to hold more nuclear talks after latest round

-
 Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show
Man City close in on Champions League thanks to Everton late show
-
Bayern close in on Bundesliga title with Heidenheim thumping

-
 Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial
Tunisia opposition figures get jail terms in mass trial
-
Putin announces 'Easter truce' in Ukraine


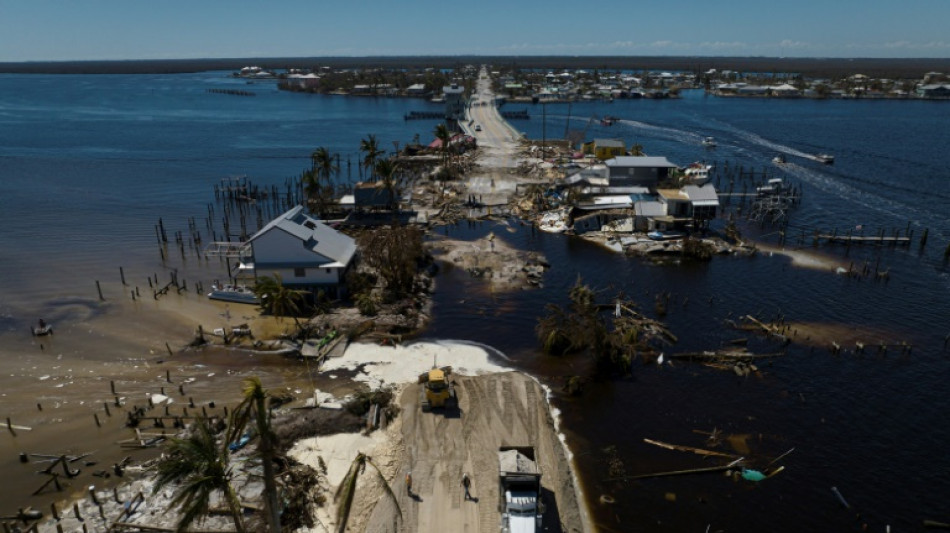
US hurricane rebuilding rules must adapt to 'era of climate change': expert
After an extreme weather event, such as Hurricane Ian which devastated parts of Florida last month, most Americans choose to rebuild rather than move to less hazardous areas.
But as climate change increases the frequency and scale of natural disasters, does US policy need to adapt?
Gavin Smith, a professor of environmental planning at the University of North Carolina, worked for several states following major hurricanes, including Katrina in Mississippi (2005) and Matthew in North Carolina (2016).
According to him, current reconstruction standards are not up to the challenges posed by climate change, but correcting them will require real "political will."
Smith's responses to AFP have been lightly edited and condensed for clarity.
- Current reconstruction rules -
Q: What are the rules for re-construction after a hurricane, and are they adapted to climate change?
A: Communities must comply with the local codes and standards in place in their jurisdiction before the storm struck.
In the US, we have the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), which has historically been subsidized by the federal government.
For a community to join the program, it has to adopt certain flood risk reduction standards. They include building codes as well as land use plans.
Then, if a home is damaged in the storm more than 50 percent of their value, it must be built back to the most recent code and standards in place.
Our standard for flood is rebuilding largely back to the "100 year flood," more accurately termed the one percent annual chance flood event. But in an era of climate change, that "100 year" flood is happening more and more often.
Most risk reduction codes and standards often reflect a climate of the past.
For example, we spent $14 billion rebuilding the levee system in New Orleans after hurricane Katrina. That levee system was built back to the "100 year flood."
So you could make the argument that in the era of climate change, that levee system is already out of date.
- Political will -
Q: What do you expect from government officials?
A: Disasters can present opportunities to rebuild communities safer.
What I'm suggesting is that if we're going to spend hundreds of millions of dollars building these communities back, we need to require communities to adopt higher codes and standards.
But that takes political will of both members of Congress and local elected officials.
These are really difficult trillion dollar questions.
You'll also have builders and the private sector saying, "We should limit those kinds of regulations, as we need to quickly rebuild."
It takes a lot of political will for a mayor or for a governor to say "No, we've got to do what's right in the long run.:
Unfortunately, people don't get elected by saying "I am going to require higher standards."
That's not a winning slogan. It takes political will to say, enough is enough, we need to adopt higher standards, it's going to take time, cost more, and people may have to pay more to do it.
That said, we also need to make sure we include equity in processes adopted to develop those standards.
The shrimpers and the crabbers that live in a very modest house on the water, if we make them adopt higher standards, can they afford it?
- Rules for resilience -
Q: Concretely, what would be these better standards?
A: A really simple way to think about it is "where" and "how" you build in relation to natural hazards, including those exacerbated by climate change.
The "how" include elevating structures, more stringent standards for wind performance, like better roof shingles, hardening our infrastructure -- communication systems, bridges, roads, levees... We can also do this by protecting natural systems like dunes and wetlands.
The "where" is what we would often refer to as land use planning.
Should we be putting a hospital, or a school, in an area subject to storm surge? Probably not.
A community may choose to say, we're not going to build a house within 200 meters of the beach.
Or adopt a gradual disinvestment strategy in extremely risky areas (managed retreat). It's very difficult to do politically, but it's happening on a small scale.
Resilience is really about a series of protective measures or choices. It's not just one. A levee, if that's your only protection and it fails, to me that's not resilience.
Y.Nakamura--AMWN